Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD), also known as Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a common yet serious condition where the arteries that supply blood to your limbs become narrowed or blocked. This restricted blood flow can lead to significant health problems, including pain, tissue damage, and, in severe cases, the risk of limb loss. As a vascular surgeon, I’ve encountered numerous patients who experience the debilitating effects of PVD, and one of the most effective treatments we often recommend is angioplasty.
Understanding Peripheral Vascular Disease
Before diving into the specifics of angioplasty, it’s crucial to understand what PVD entails. PVD is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits build up on the inner walls of the arteries, reducing blood flow. This reduced blood flow can result in symptoms such as leg pain when walking (claudication), numbness, or even sores that won’t heal.
If left untreated, PVD can progress, leading to more severe complications, including critical limb ischemia, which may necessitate amputation. Therefore, early diagnosis and intervention are vital to preventing these outcomes.
What is angioplasty?
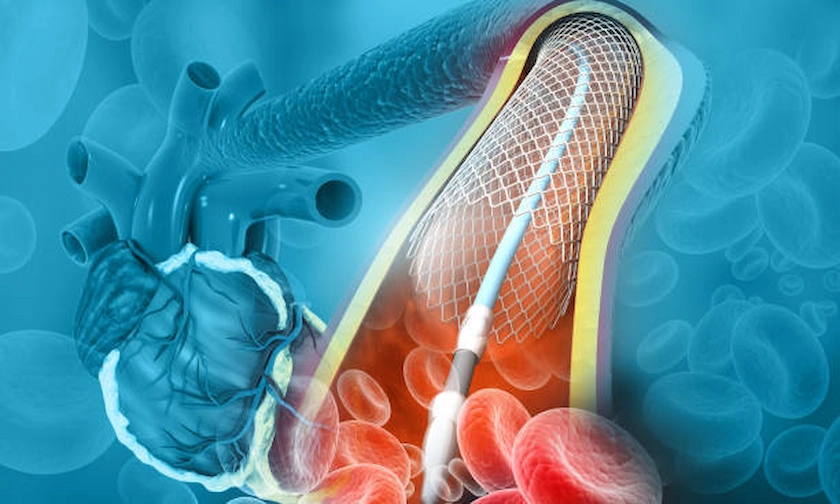
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to open up narrowed or blocked arteries, allowing blood to flow more freely. During the procedure, a small balloon is inserted into the artery via a catheter and then inflated at the site of the blockage. The balloon pushes the plaque against the artery walls, widening the artery and restoring blood flow. In many cases, a stent, a small wire mesh tube, is also placed in the artery to keep it open.
This procedure is particularly effective for patients with PVD, as it directly addresses the issue of restricted blood flow, alleviates symptoms, and improves quality of life. It is often performed on an outpatient basis, meaning most patients can return home the same day.
The Role of Angioplasty in Treating PVD
Angioplasty plays a critical role in the management ofPVD. For many patients, lifestyle changes and medications may not be enough to manage symptoms. When these conservative measures fail, angioplasty provides a viable alternative to more invasive surgeries. The procedure can be tailored to the specific needs of the patient, targeting the exact location of the blockage with precision.
One of the significant benefits of angioplasty is its ability to provide immediate relief from the symptoms of PVD. Patients often report reduced pain, increased mobility, and an overall improvement in their daily lives soon after the procedure.
Risks and Considerations
Like any medical procedure, angioplasty carries some risks. These may include bleeding, infection, or a reaction to the contrast dye used during the procedure. There is also a small chance that the artery could narrow over time, a condition known as restenosis. However, advances in technology and the use of drug-eluting stents (which release medication to help prevent restenosis) have significantly reduced these risks.
As a vascular surgeon, I always discuss these potential risks with my patients, ensuring they fully understand the procedure and what to expect. It’s essential to weigh the benefits of improved blood flow and symptom relief against the risks to make an informed decision.
Long-term Management of PVD After Angioplasty
Angioplasty is highly effective, but it is not a cure for PVD. Long-term management is crucial to prevent recurrence and further complications. This includes lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet, and engaging in regular physical activity. Medications to control cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels may also be prescribed.
In addition, regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor the condition of the treated artery and ensure that blood flow remains unobstructed. These visits may include ultrasound or other imaging tests to check for signs of restenosis.
For a more in-depth understanding of how we manage vascular conditions, explore the vascular care approach that we adopt. It’s designed to cater to each patient’s unique needs and ensure comprehensive care.
Conclusion
Angioplasty is a powerful tool in the treatment of peripheral artery disease, offering relief from symptoms and preventing serious complications. If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of PVD, it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly. Early intervention can make a significant difference in outcomes.
As always, my goal is to provide the highest level of care to my patients. If you’re dealing with PVD or have concerns about your vascular health, consider learning more about the treatments available that can help restore your well-being. Additionally, I am always available to discuss your individual situation and how we can work together towards improving your vascular health. Feel free to reach out if you have any questions or need further guidance.
Your vascular health is vital, and with the right approach, we can manage and treat PVD effectively, allowing you to lead a healthier life.