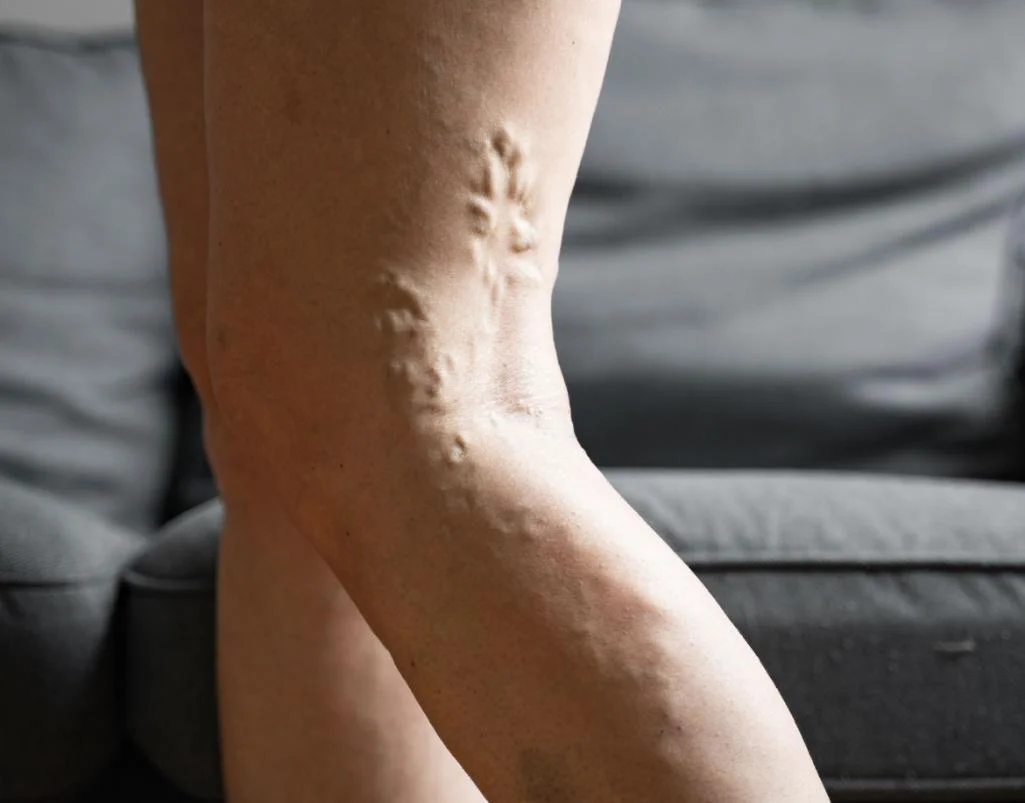
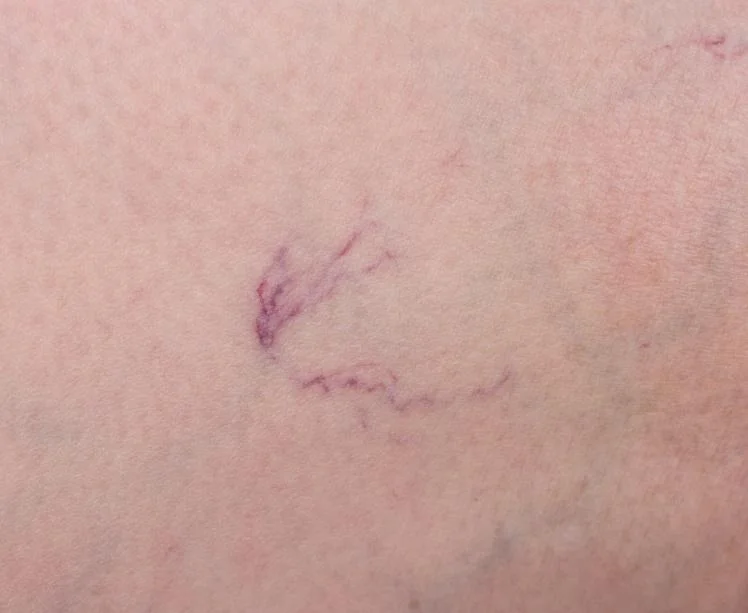
If you’ve been told to try compression stockings or are browsing online wondering whether they’re worth it, you’re not alone. Many people dealing with varicose veins want to know if these snug-fitting socks actually do anything — or if they’re just tight and uncomfortable.
Here’s a practical look at what compression stockings can (and can’t) do, how to choose the best type, and whether they’re a good fit for your situation.
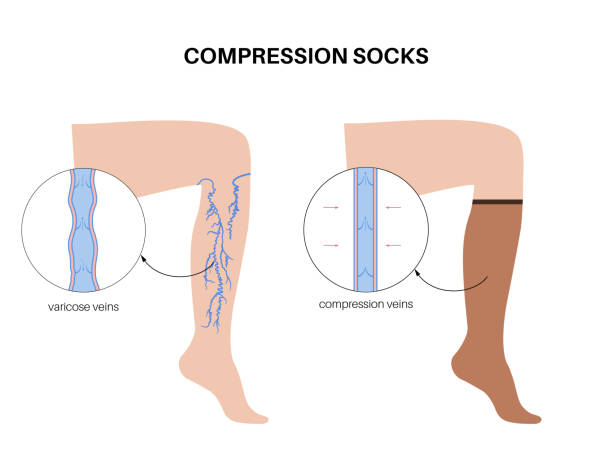
Do Compression Socks Help Varicose Veins?
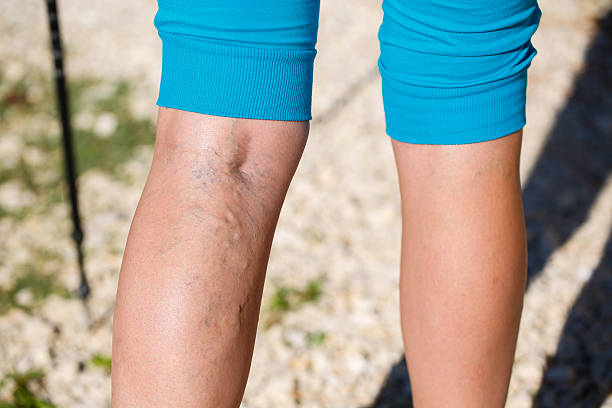
Yes — compression socks do help varicose veins, particularly when it comes to managing symptoms. They gently squeeze the legs, which improves circulation, reduces swelling, and helps with feelings of heaviness or aching.
That said, they don’t treat the root cause. Once the stockings come off, symptoms often return. They’re best seen as a support measure, not a cure.
In short:
✅ Help relieve discomfort and swelling
✅ Support better blood flow
❌ Don’t eliminate varicose veins
❌ Don’t solve the underlying root cause
What Are Varicose Vein Compression Stockings?
Varicose vein compression stockings are specially designed to provide graduated compression — meaning the pressure is highest at the ankle and gradually decreases up the leg. This encourages upward blood flow, countering the effects of gravity.
They come in different lengths (knee-high, thigh-high, full tights) and different compression levels. Some are available over the counter, while others are prescribed by a doctor for more specific medical needs.
Choosing the Best Compression Stockings for Varicose Veins
There’s no one-size-fits-all, but a good pair of stockings should provide the right level of support, feel comfortable enough to wear daily, and be suitable for your specific needs.
When selecting varicose vein compression stockings, consider the following:
1. Compression Level (mmHg)
Compression stockings are categorised into classes based on the pressure they provide, measured in millimetres of mercury (mmHg). The appropriate class depends on the severity of your condition and your doctor’s recommendation:
- Class 1 (15–20 mmHg): Light compression for tired legs, mild swelling, or early-stage varicose veins. Often used during pregnancy, travel, or long hours of sitting or standing.
- Class 2 (20–30 mmHg): Moderate compression for moderate to severe varicose veins, more noticeable swelling, or post-treatment support. Also commonly used to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Class 3 (30–40 mmHg): Firm compression reserved for severe venous insufficiency, lymphedema, or advanced circulatory problems. This level should only be used under medical supervision.
Always consult your doctor before using higher-class stockings to ensure they’re safe and appropriate for your condition.
2. Stocking Length
The right length depends on the location and extent of your vein symptoms:
- Knee-high: Covers the lower leg and is suitable for most common varicose vein cases
- Thigh-high: Provides support for upper leg veins or deeper circulation issues
- Pantyhose/Tights: Offers full-leg support — helpful during pregnancy or for people with widespread symptoms
- Open-toe vs. Closed-toe: Open-toe stockings offer better breathability and can be worn with sandals; closed-toe versions provide full foot coverage and warmth
3. Material and Fit
Comfort makes a huge difference — especially if you’ll be wearing stockings all day.
- Choose breathable, moisture-wicking fabrics to prevent overheating and irritation
- Stockings should fit snugly but not dig in or cut off circulation
- Look for seamless or hypoallergenic options if you have sensitive skin
- They should be easy to put on and take off — poorly fitting stockings often end up unused
When Are Compression Stockings Most Useful?
Compression stockings are especially helpful if:
- You’re standing or sitting for long hours
- You’re recovering from vein treatment
- You’re managing mild swelling or discomfort
- You’re pregnant or prone to leg fatigue
They’re most often used to ease symptoms or prevent progression, particularly if you’re not yet ready for a procedure — or want to maintain results after one.
When to See a Doctor
While compression stockings help manage symptoms, medical intervention may be needed if you experience:
- Severe pain, swelling, or heaviness in the legs
- Skin discolouration, ulcers, or open sores near varicose veins
- Bleeding from a varicose vein
- No relief despite wearing compression stockings regularly
A vascular surgeon can recommend the best treatment plan, including minimally invasive procedures to treat the underlying vein problem and provide long-term relief.
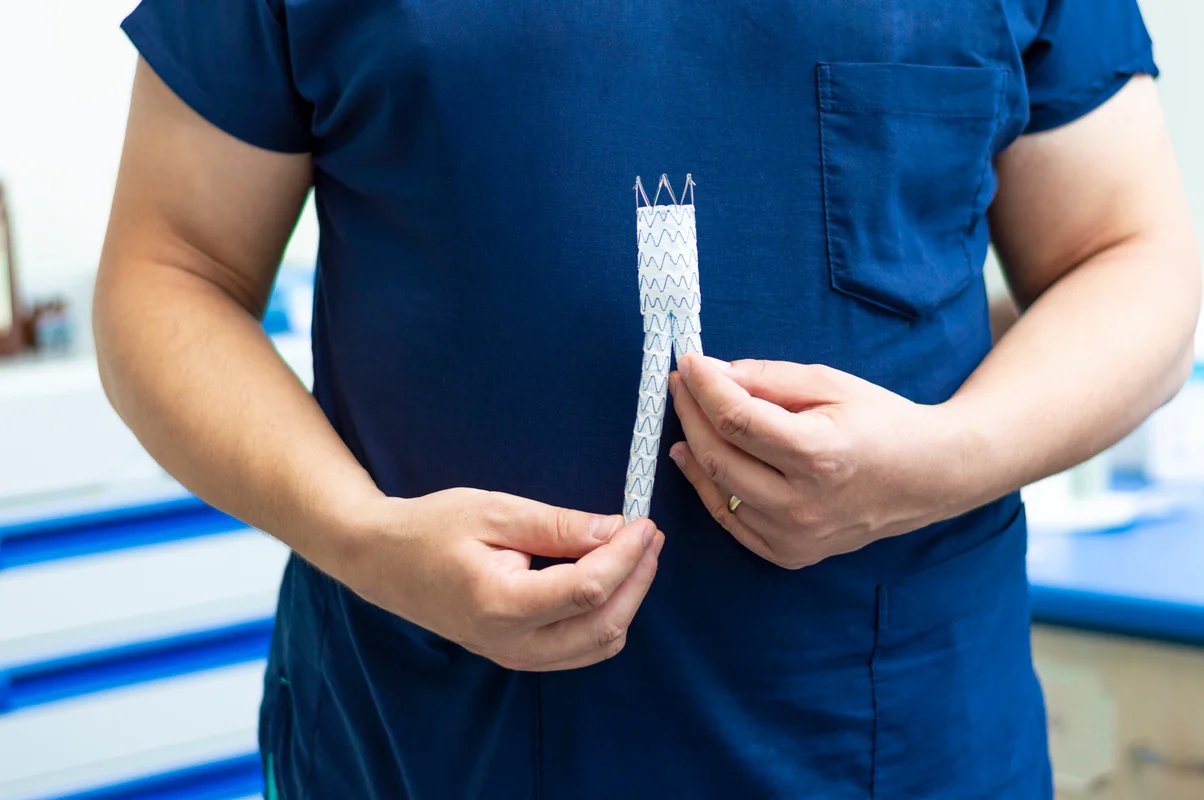
What If I Want to Get Rid of the Veins Completely?
While stockings help manage symptoms, they don’t remove varicose veins. If you’re after long-term results, consider discussing treatment options such as:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
- ClariVein
- VenaSeal
- Sclerotherapy
- Microphlebectomy
These are minimally invasive options that target the underlying vein issues — with short recovery times and lasting results.
Struggling with Varicose Veins?
Explore safe and effective treatment options with Dr. Darryl Lim.

Final Thoughts
Compression stockings are a useful tool in managing varicose veins. They reduce swelling, improve comfort, and support circulation — especially when worn consistently. Just be aware that they’re a form of symptom control, not a cure.
In Singapore’s hot and humid climate, wearing them all day can be tricky. If they’re uncomfortable or not helping, it may be time to explore longer-term solutions.
If you need guidance on selecting the right compression stockings or want to explore medical treatment options, schedule a consultation with Dr. Darryl Lim for expert vein care and personalized recommendations.
FAQ
Do compression socks help varicose veins go away?
No — they help with symptoms like swelling and heaviness, but don’t remove the veins themselves. Once taken off, symptoms can return.
How long should I wear compression stockings each day?
Most people wear them during the day and remove them at night. Follow your doctor’s advice, especially after procedures.
Are there any downsides to wearing them?
Wearing the wrong size or compression level can cause discomfort. In conditions like peripheral arterial disease, compression stockings may not be safe, as they can potentially reduce blood flow to the feet.
Always check with your vascular specialist before starting compression therapy — especially if you have other underlying circulation issues.