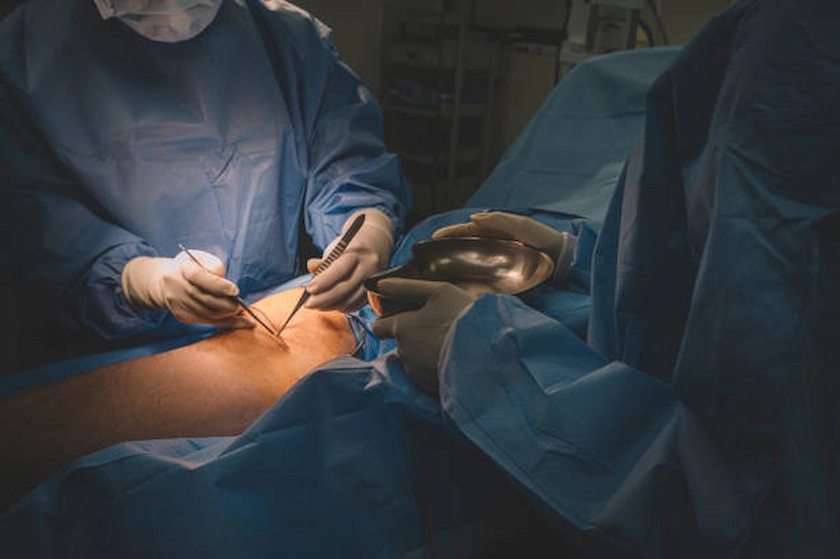
Endovascular surgery is a minimally invasive procedure focused on treating vascular diseases through the blood vessels. Utilizing advanced imaging techniques, surgeons guide catheters and other tiny instruments through small incisions, often in the groin, to diagnose and treat conditions such as aneurysms, blood clots, and arterial blockages. Common procedures include angioplasty and stenting, endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR), thrombectomy, and embolization. These techniques offer patients shorter recovery times, reduced pain, and lower risks of complications compared to traditional open surgery, making endovascular surgery an increasingly preferred option for vascular treatment.
What is endovascular surgery?
Endovascular surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat problems affecting the blood vessels, such as aneurysms, blood clots, and peripheral artery disease. Unlike traditional open surgery, endovascular surgery involves making small incisions and using catheters and other instruments to repair the blood vessels from within.
History of Endovascular Surgery
Endovascular surgery has evolved significantly over the past few decades. It began in the 1960s with the development of angioplasty and stenting techniques, which revolutionized the treatment of vascular diseases. Advances in imaging technology and the development of specialized tools have further expanded the scope and success of endovascular procedures.
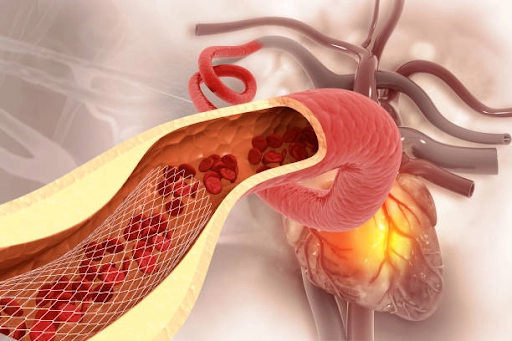
Common Endovascular Procedures
Angioplasty and Stenting: This procedure involves using a balloon-tipped catheter to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels, typically due to atherosclerosis or plaque build-up. The balloon is inflated at the site of the blockage to widen the vessel, and a stent (a small wire mesh tube) may be placed in the vessel to keep it open and prevent re-narrowing.
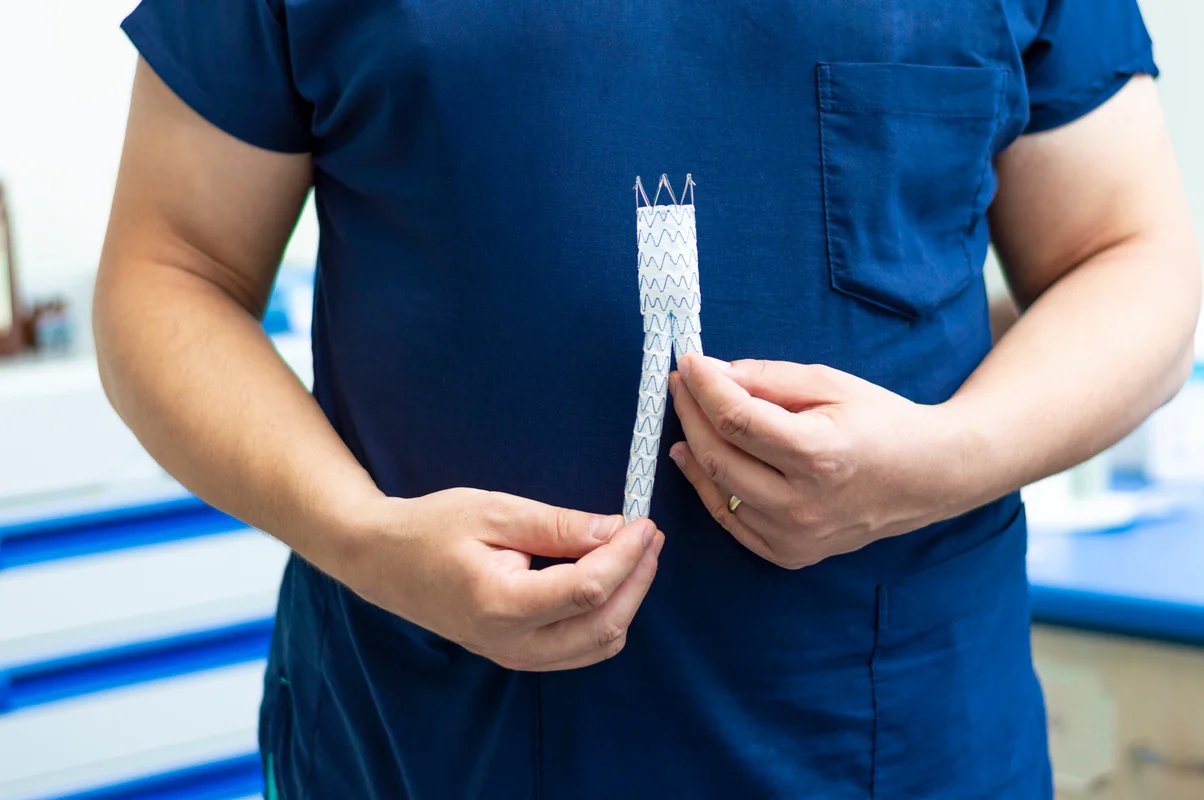
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR): Used to repair aortic aneurysms, this minimally invasive procedure involves placing a graft (a fabric tube supported by a metal mesh) inside the affected artery via a catheter inserted through a small incision in the groin. The graft reinforces the weakened vessel wall, reducing the risk of rupture and allowing blood to flow through the graft instead of the aneurysm.
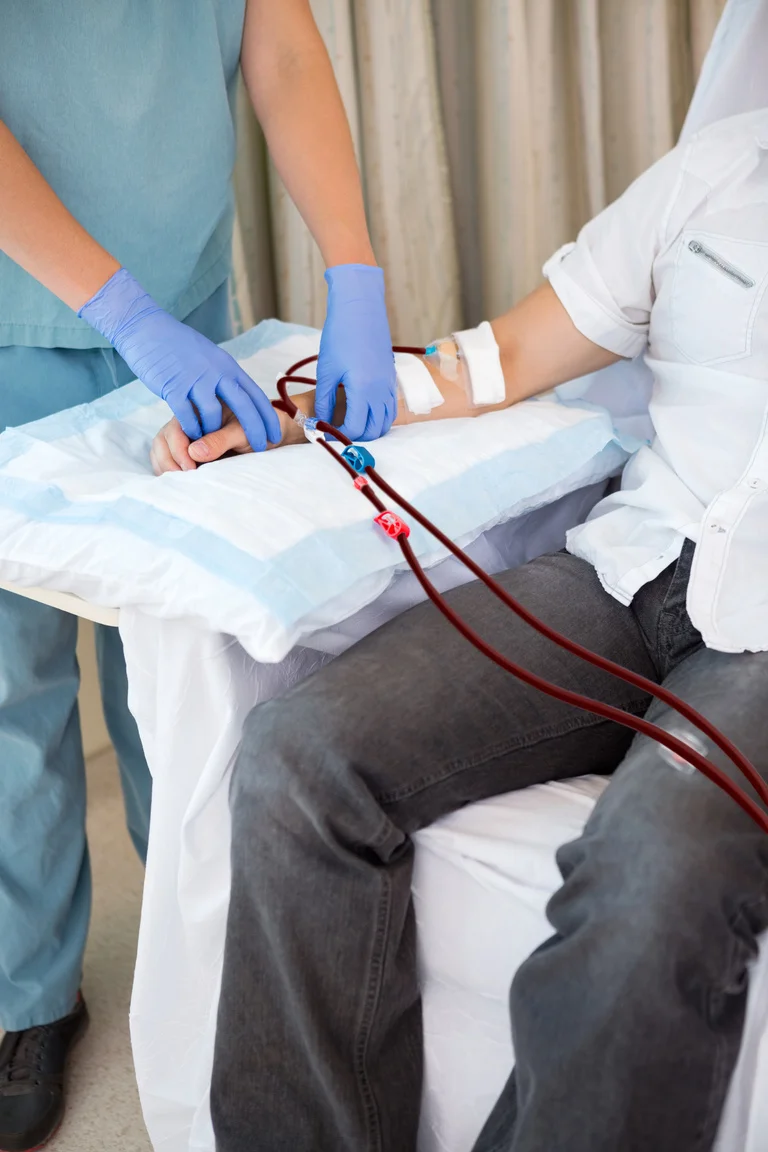
Thrombectomy: This procedure removes blood clots from blood vessels to restore normal blood flow. A catheter is inserted into the affected vessel, and various techniques, such as mechanical clot retrieval devices or suction, are used to remove the clot. A thrombectomy is often performed in cases of acute stroke or deep vein thrombosis.
Embolization: Used to block abnormal blood vessels, such as those feeding a tumor, this procedure involves injecting substances (such as tiny beads, coils, or liquid agents) through a catheter into the targeted vessel. This obstructs blood flow to the abnormal area, which can shrink tumors, control bleeding, or treat arteriovenous malformations.
Atherectomy: This procedure removes plaque from the interior of an artery to restore normal blood flow. A catheter with a rotating blade, laser, or other device is used to shave, vaporize, or cut away the plaque. Atherectomy is often performed on peripheral arteries in the legs or coronary arteries.
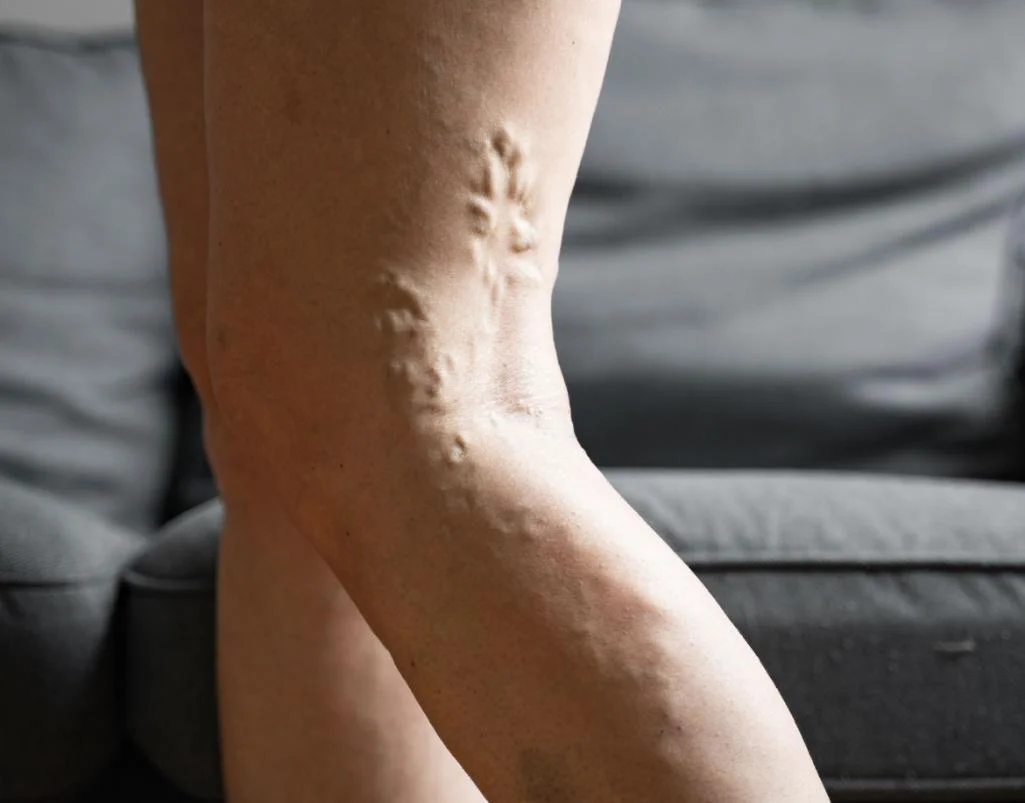
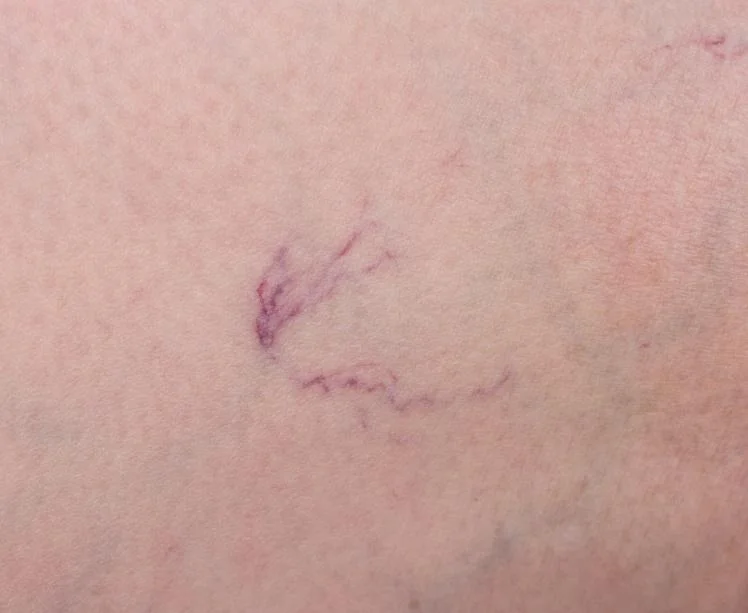
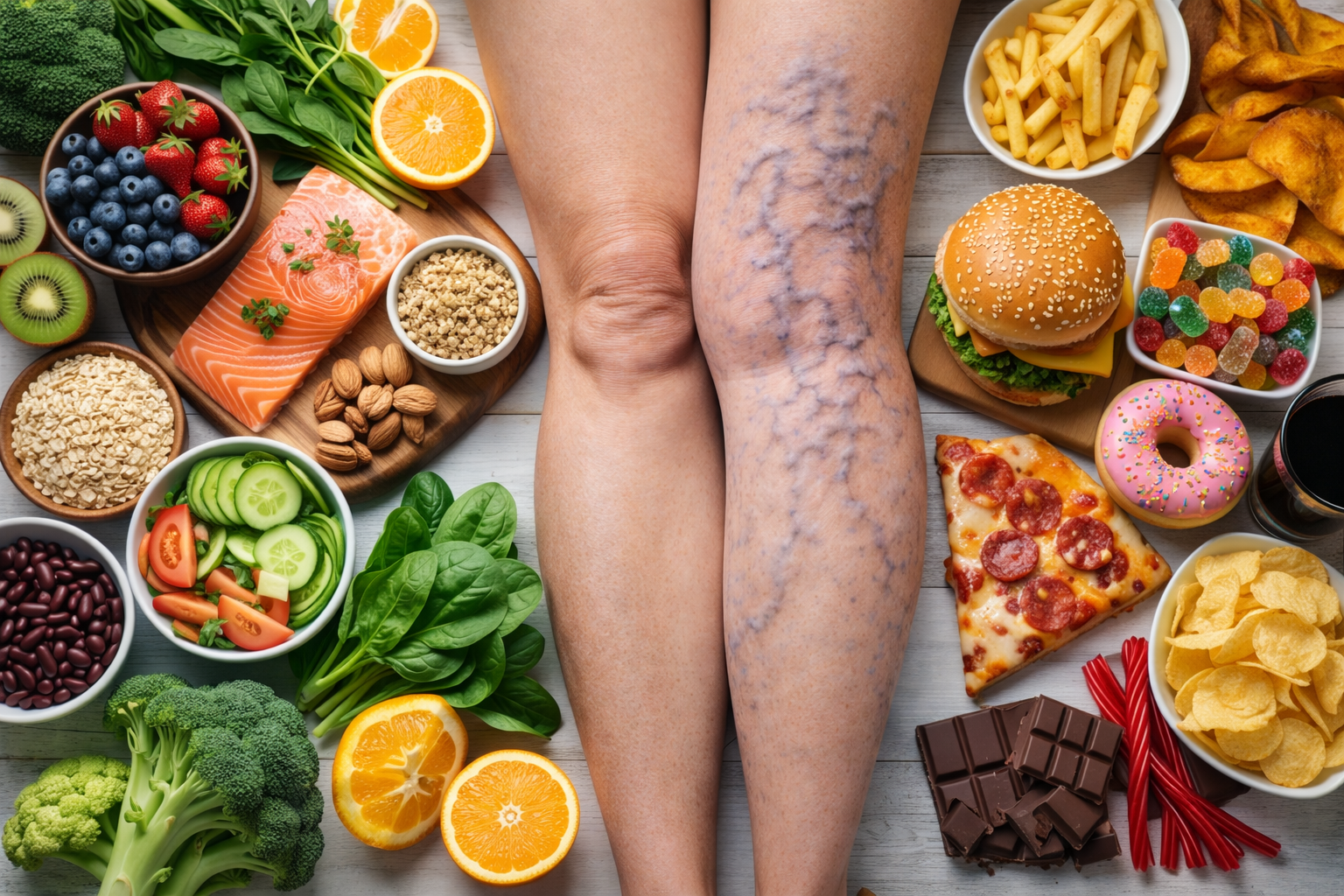
Varicose Vein Ablation: This minimally invasive procedure treats varicose veins by closing off the affected veins. A catheter is inserted into the vein, and heat (radiofrequency or laser) is applied to collapse and seal the vein. Blood is then rerouted to healthier veins, reducing symptoms and improving appearance.
Carotid Artery Stenting: This procedure is used to treat carotid artery disease, where the carotid arteries (major blood vessels in the neck supplying blood to the brain) become narrowed or blocked. A stent is placed in the artery to keep it open and improve blood flow to the brain, reducing the risk of stroke.
Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT): This procedure treats varicose veins by using laser energy delivered through a catheter to heat and close off the affected veins. The vein shrinks and eventually gets absorbed by the body, rerouting blood flow to healthier veins.
Peripheral Artery Angioplasty: Similar to coronary angioplasty, this procedure treats narrowed or blocked arteries outside of the heart, such as those in the legs or kidneys. A balloon catheter is used to widen the artery, and a stent may be placed to keep it open, improving blood flow to the affected area.
These endovascular procedures offer less invasive alternatives to traditional surgery, often resulting in shorter recovery times and fewer complications.
Benefits of Endovascular Surgery
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Endovascular surgery offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
Smaller incisions: This reduces the risk of infection and speeds up recovery time.
Less pain and scarring: Patients experience less postoperative pain and minimal scarring due to not needing open surgery or any large incisions.
Shorter Hospital Stays: Many endovascular procedures are performed on an outpatient basis or require only a short hospital stay, as there are usually no large wounds which require monitoring post operatively.
Faster Recovery: Patients can typically return to their normal activities more quickly compared to traditional surgery.
Need Minimally Invasive Surgery?
Modern endovascular techniques offer effective solutions without major incisions. Experience faster recovery and reduced downtime.

Conclusion
Endovascular surgery is a transformative approach to treating vascular conditions, offering numerous benefits due to its minimally invasive nature. With ongoing advancements in technology and techniques, the scope of endovascular procedures continues to expand, providing effective treatment options for patients with various vascular diseases.