Recognizing and treating Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is critical to preventing potentially life-threatening complications such as pulmonary embolism. DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs, causing symptoms like swelling, pain, tenderness, redness, and warmth in the affected area. Prompt diagnosis is essential, often involving ultrasound imaging and blood tests. Treatment aims to prevent clot growth and new clot formation, typically through anticoagulant medications, thrombolytic therapy, or in some cases, surgical intervention. Compression stockings and lifestyle changes may also be recommended to improve circulation and prevent recurrence. Early recognition and comprehensive treatment of DVT are key to reducing the risk of serious complications and ensuring better patient outcomes.
Understanding DVT
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. DVT can cause leg pain or swelling but can also occur with no symptoms. It’s a serious condition because blood clots in your veins can break loose, travel through your bloodstream, and lodge in your lungs, blocking blood flow (pulmonary embolism).
Causes of DVT
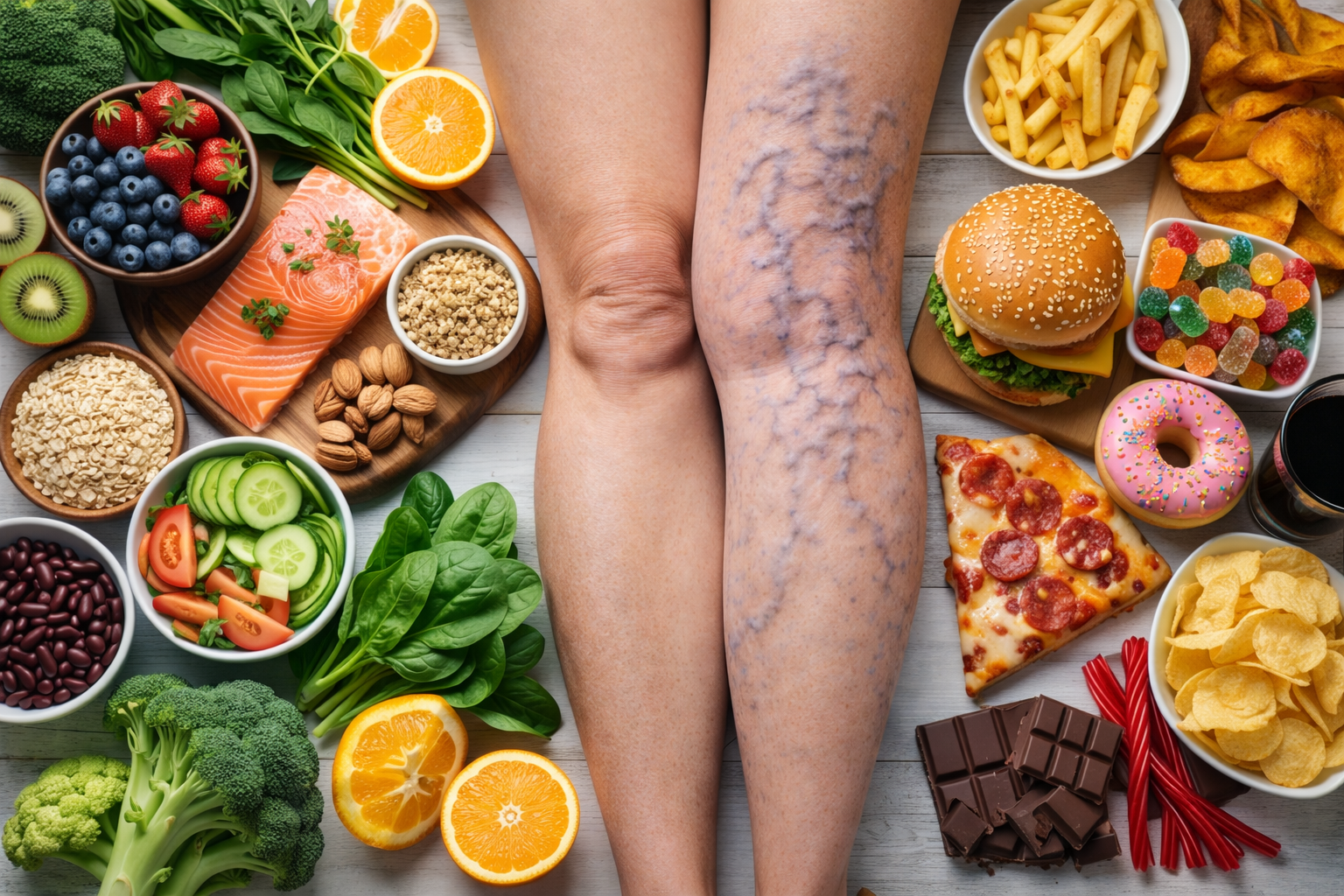
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is primarily caused by factors that affect normal blood flow and clotting mechanisms. Prolonged immobility, such as long flights or bed rest, can lead to decreased blood flow in the legs, increasing the risk of clot formation. Medical conditions like cancer, heart disease, and inflammatory disorders also elevate the risk due to their impact on blood vessels and clotting. Hormonal changes from pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy can contribute to clot development as well. Additionally, surgeries, particularly those involving the pelvis, hips, or legs, can damage blood vessels and prompt clotting. Genetic predispositions, such as clotting disorders, and lifestyle factors like smoking, obesity, and dehydration further exacerbate the risk. Understanding these causes is essential for prevention and effective management of DVT.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase your risk of developing DVT, including:
- Prolonged Bed Rest or Inactivity: Long periods of inactivity, such as after surgery or during long trips, can slow blood flow in your legs.
- Injury or Surgery: Injury to veins or surgery can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Certain Medications: Birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Chronic Medical Conditions: Such as heart disease, lung disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Genetics: Family history of DVT or clotting disorders.
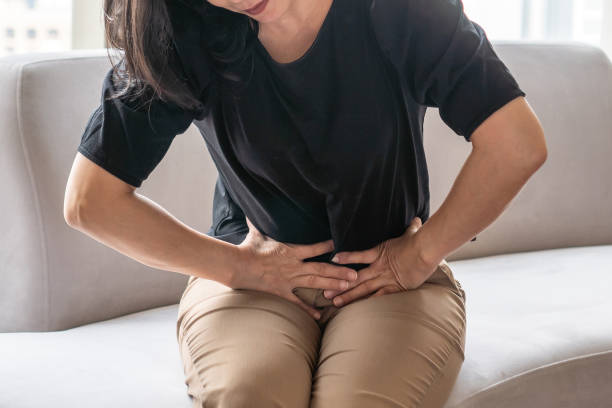
Recognizing Symptoms
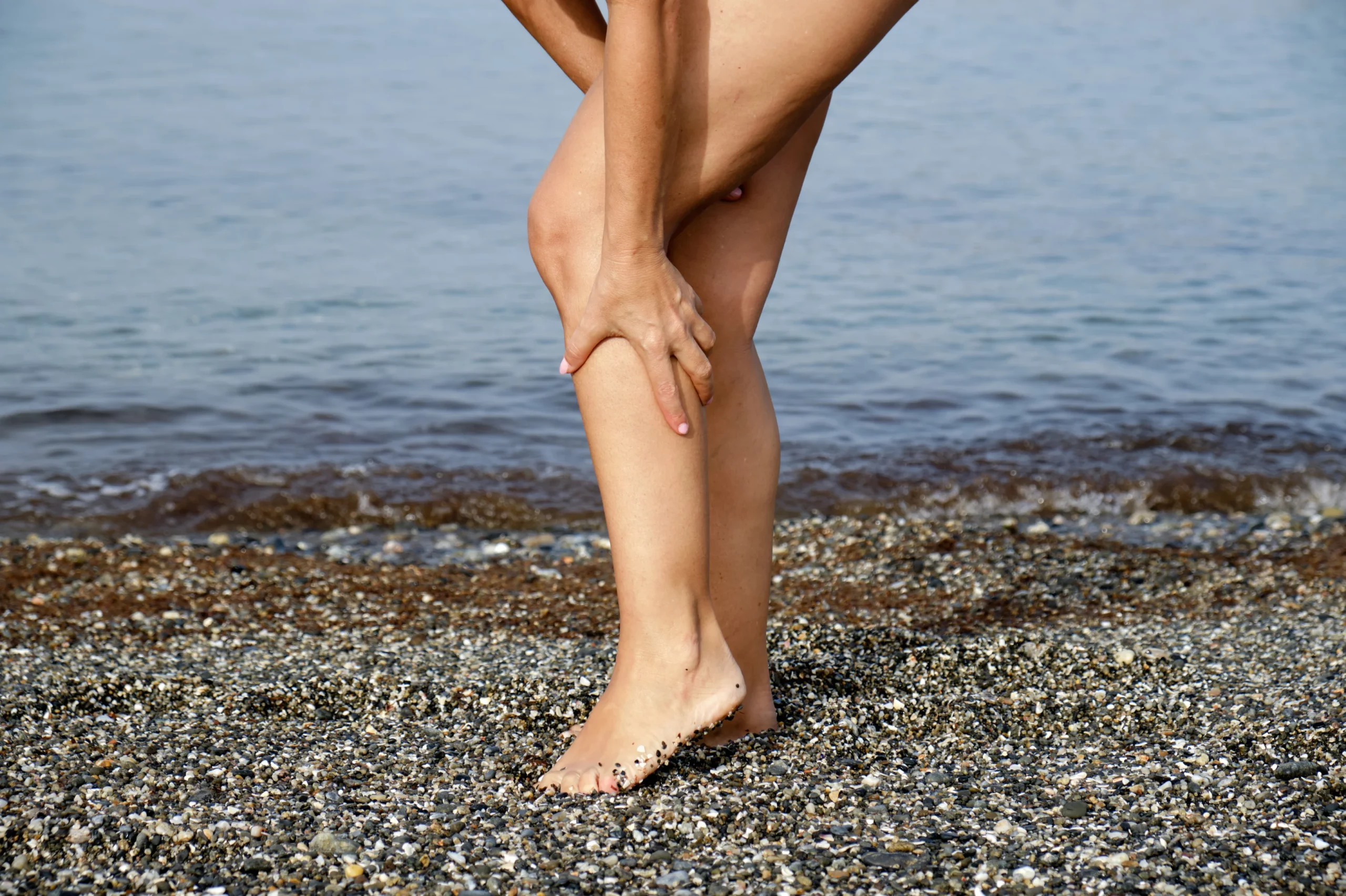
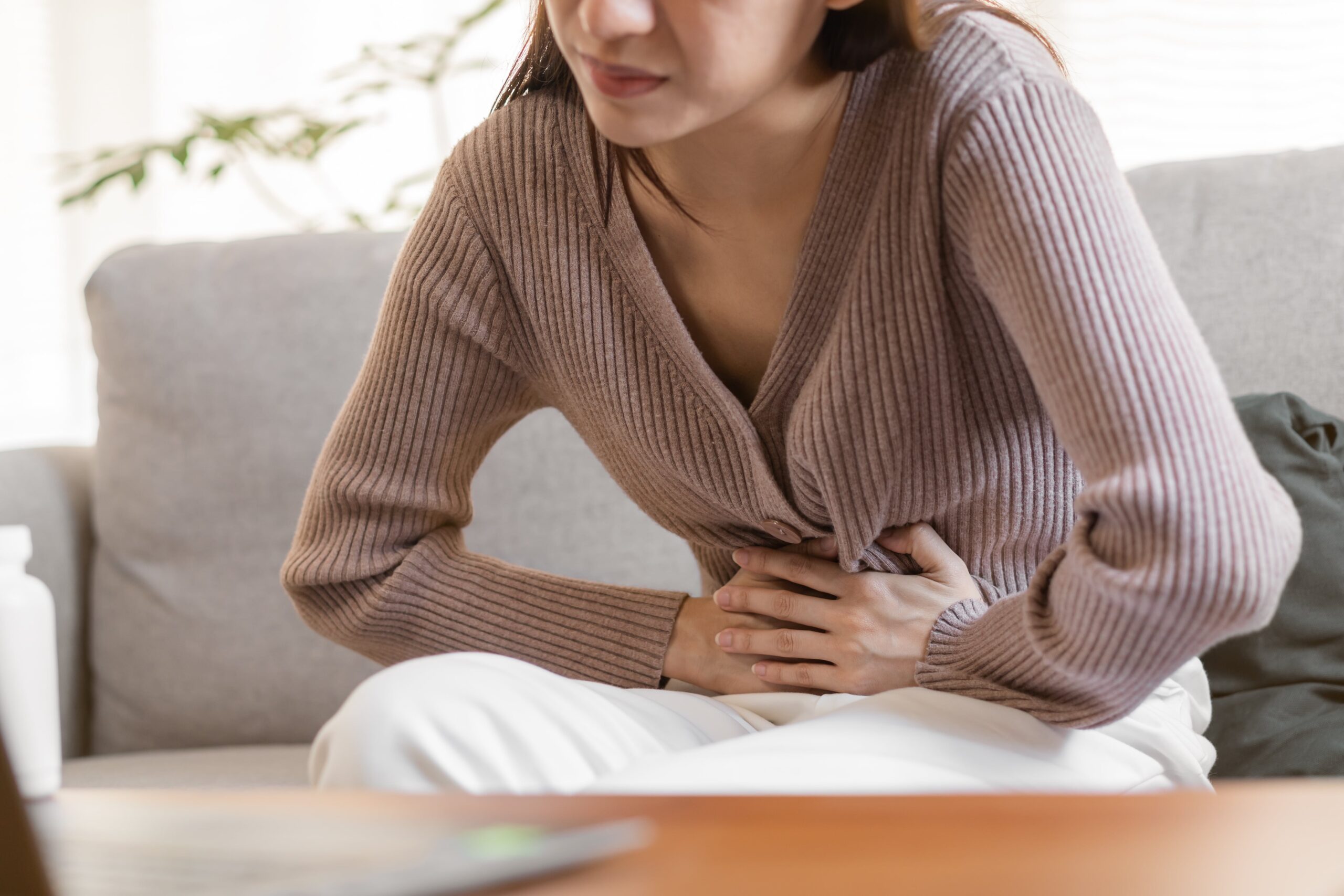
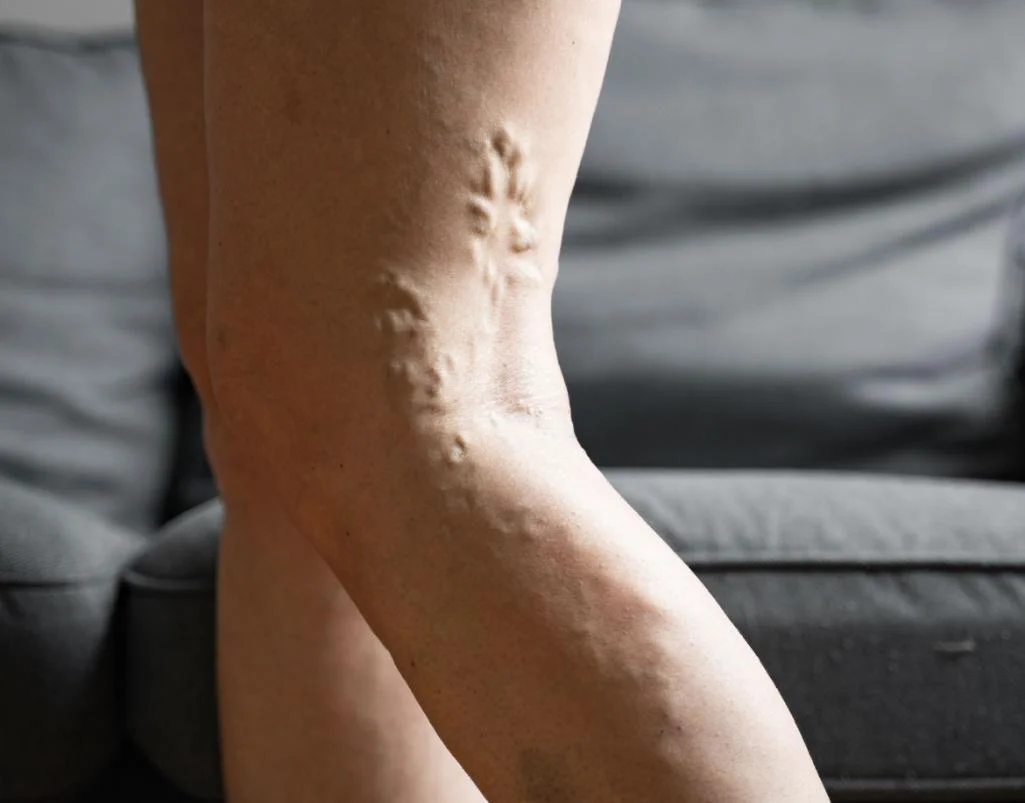
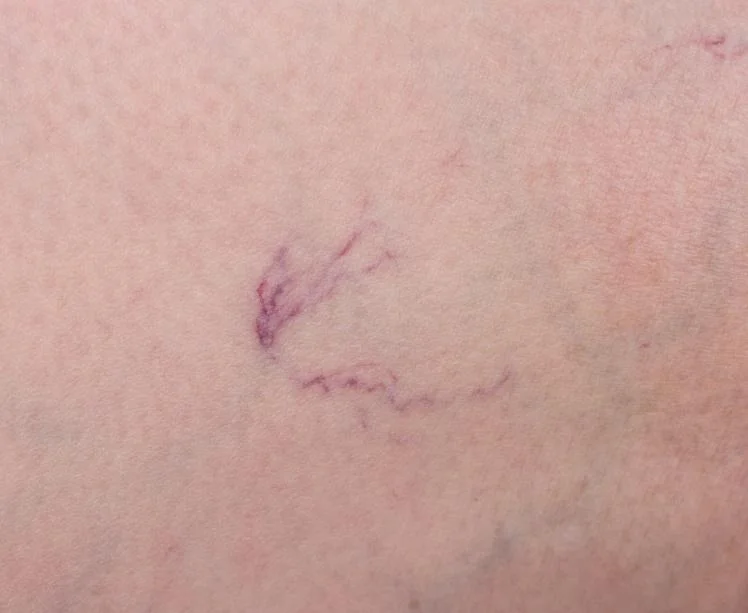
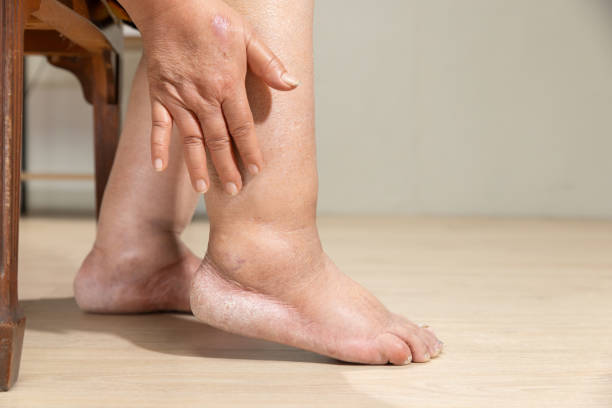
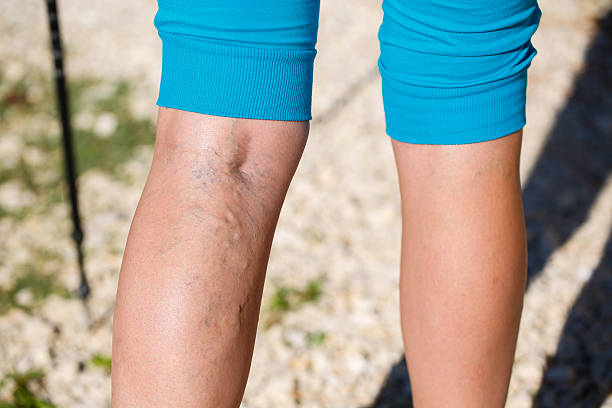
Recognizing the symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include swelling in one leg, often accompanied by pain or tenderness, which may feel like a cramp or soreness. The affected area might also display redness or discoloration and feel warm to the touch. In some cases, individuals may experience more subtle symptoms like a heavy or aching sensation in the leg. It’s important to note that DVT can sometimes occur without noticeable symptoms, making regular check-ups essential for those at risk. Prompt medical attention upon noticing these symptoms is vital to prevent complications such as pulmonary embolism, where a blood clot travels to the lungs, posing a serious health threat.
Common Symptoms
DVT symptoms can vary and might include:
- Swelling in One or Both Legs: Typically occurs in the calf.
- Pain or Tenderness in Your Leg: May start in the calf and feel like cramping or soreness.
- Warmth in the Affected Leg: The area around the clot may feel warmer than the surrounding skin.
- Red or Discolored Skin: The skin over the affected area might be red or discolored.
- Visible Veins: Surface veins may become more visible.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help immediately if you experience:
- Sudden Chest Pain: This could be a sign of a pulmonary embolism.
- Difficulty Breathing: Also indicative of a potential pulmonary embolism.
- Rapid Pulse: Another symptom that could suggest a pulmonary embolism.
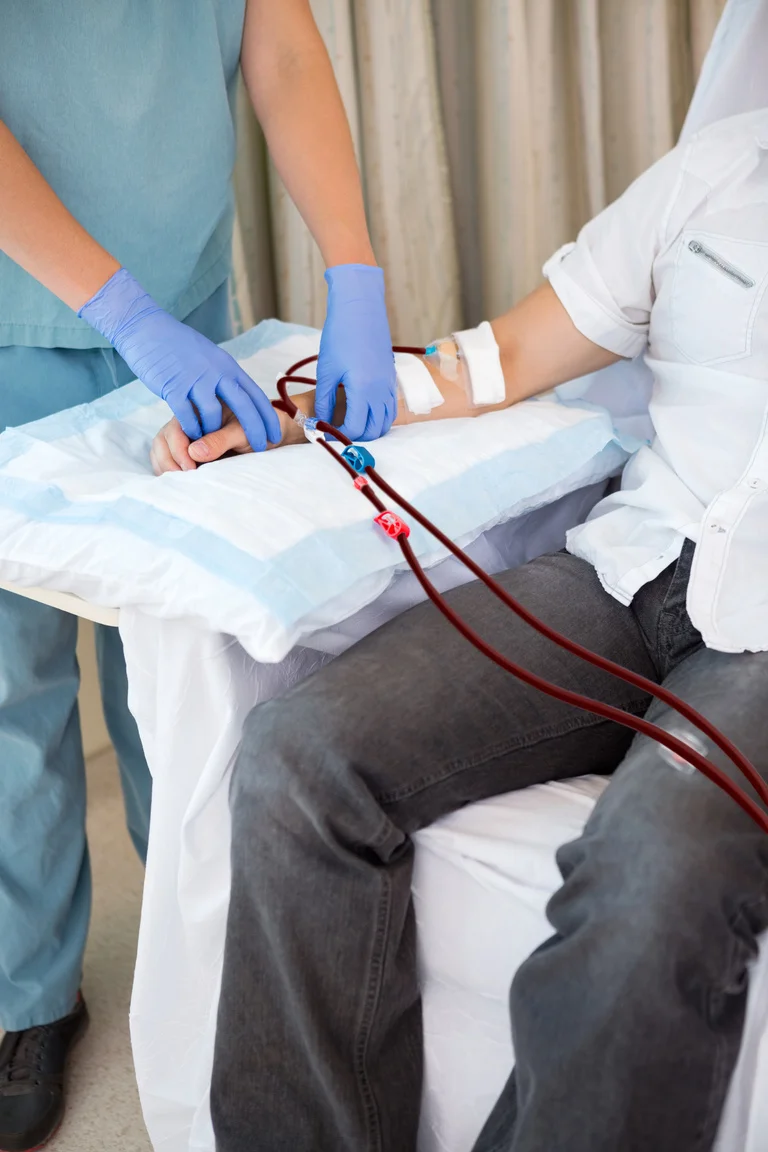
Treatment Options for DVT
Recognizing the symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include swelling in one leg, often accompanied by pain or tenderness, which may feel like a cramp or soreness. The affected area might also display redness or discoloration and feel warm to the touch. In some cases, individuals may experience more subtle symptoms like a heavy or aching sensation in the leg. It’s important to note that DVT can sometimes occur without noticeable symptoms, making regular check-ups essential for those at risk. Prompt medical attention upon noticing these symptoms is vital to prevent complications such as pulmonary embolism, where a blood clot travels to the lungs, posing a serious health threat.
Medications
Several medications can help manage DVT:
- Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners): These medications decrease the blood’s ability to clot, preventing existing clots from getting bigger and new ones from forming.
- Thrombolytics: These drugs dissolve large clots and are used in severe cases. They are administered intravenously or through a catheter directly into the clot.
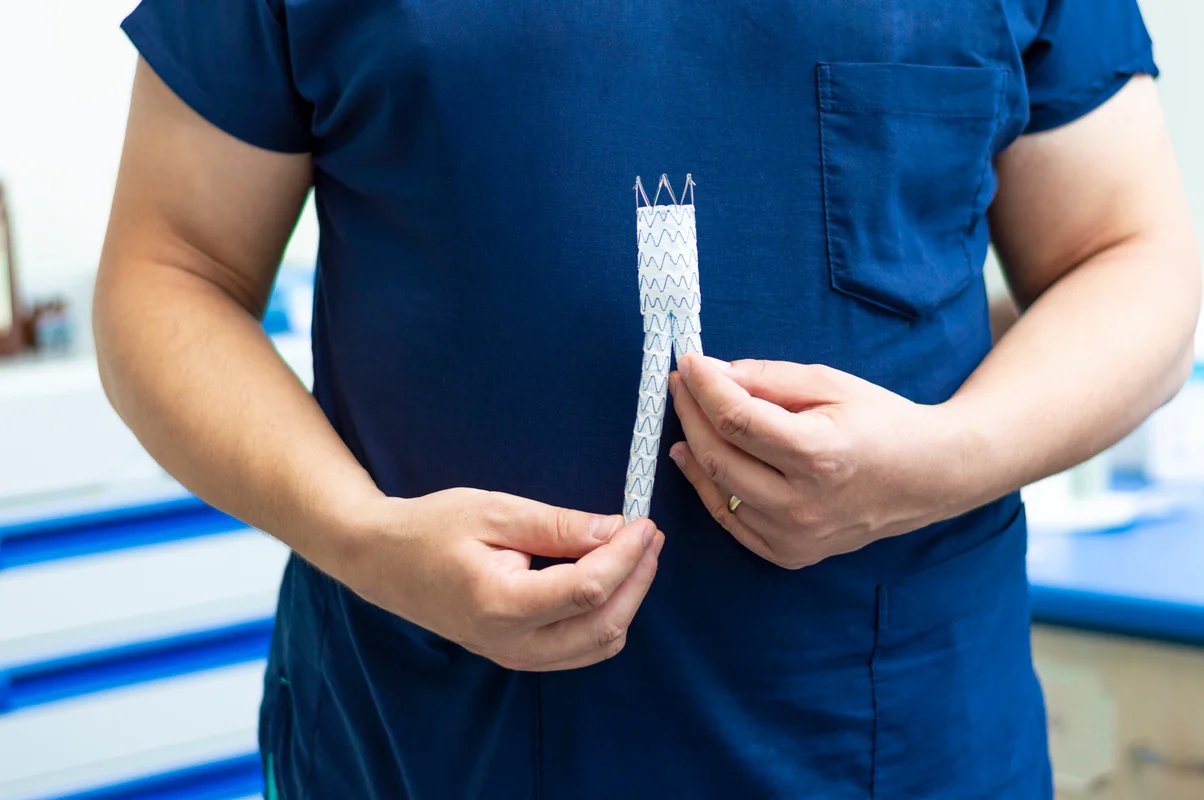
Surgical Treatments
In some cases, surgery may be necessary:
- Thrombectomy: Surgical removal of a blood clot.
- Placement of a Filter in the Vena Cava: A filter can prevent clots that break loose from lodging in the lungs.
Conclusion
Recognizing and treating DVT promptly is crucial to prevent serious complications such as pulmonary embolism. Awareness of the risk factors and symptoms, along with early medical intervention, can significantly reduce the risks associated with DVT. Always consult a healthcare provider if you suspect you have DVT or are at risk.