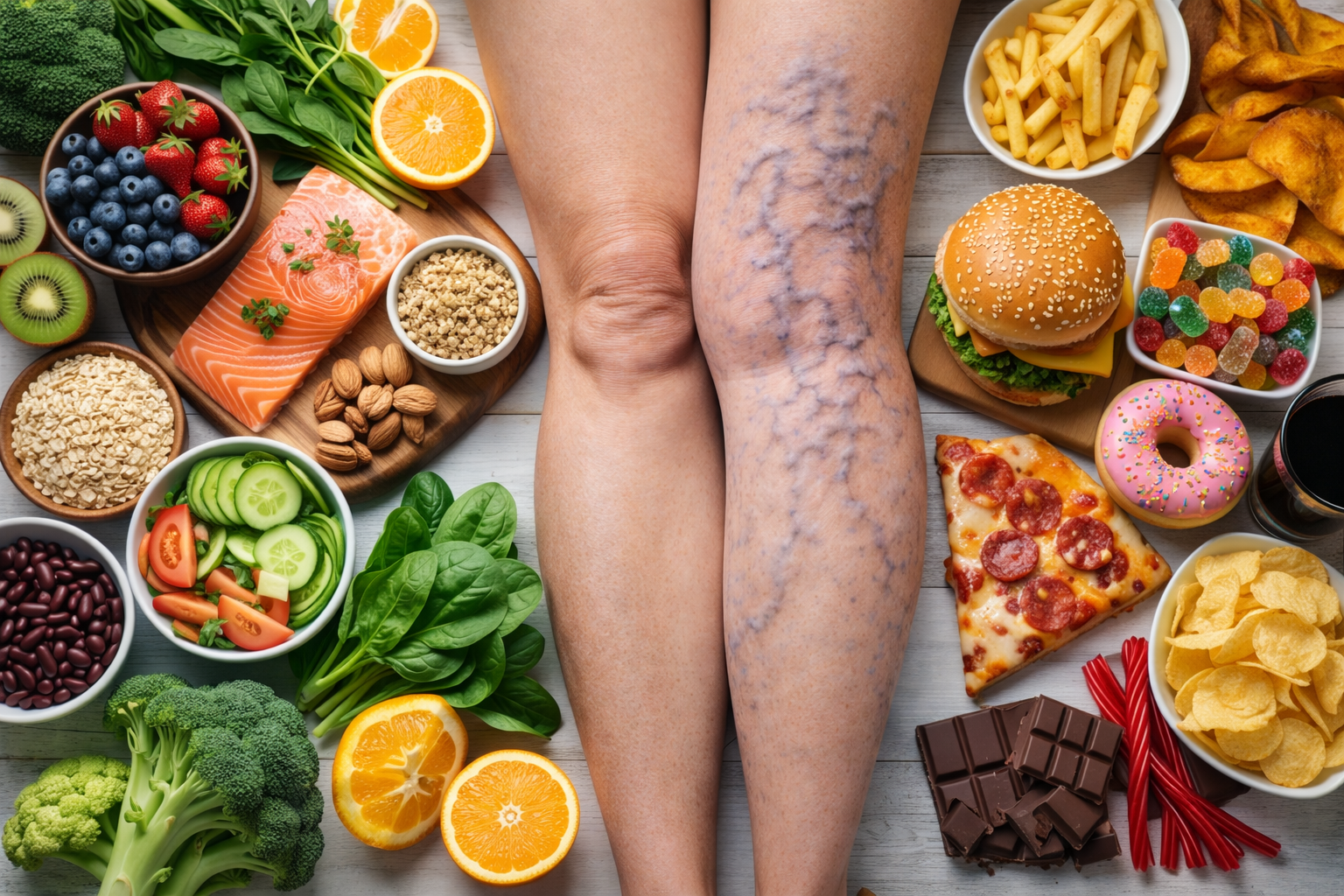
Varicose veins are a common vascular condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing discomfort and aesthetic concerns. Understanding the underlying causes, identifying symptoms, and exploring treatment options are crucial steps in managing this condition effectively. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of varicose veins, shedding light on their causes, symptoms, and various treatment modalities available to alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life.
What are varicose veins?
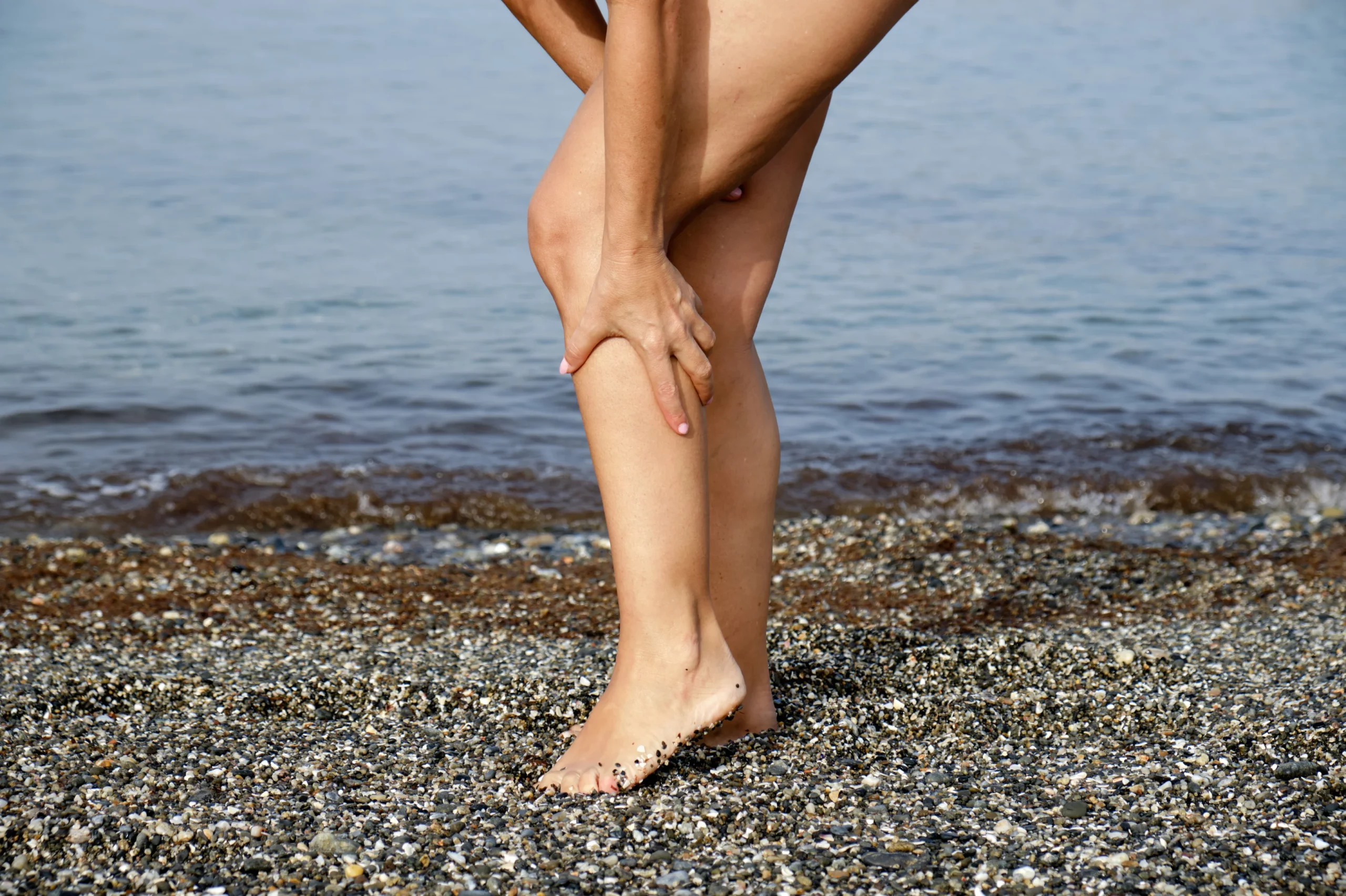
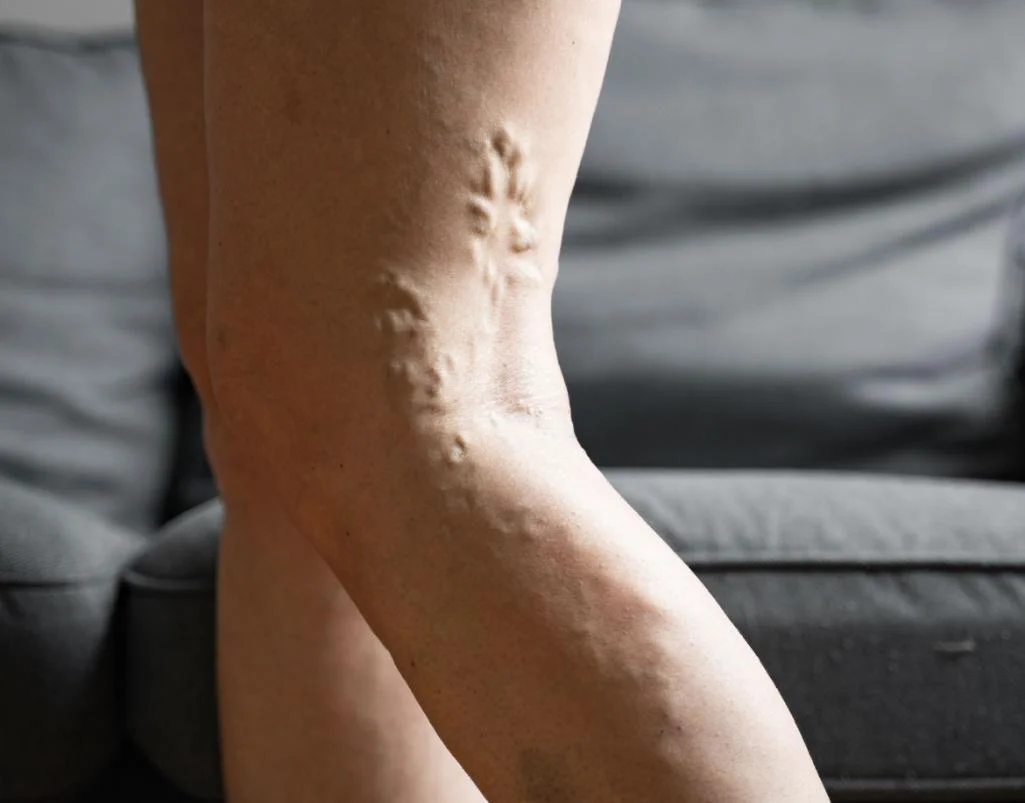
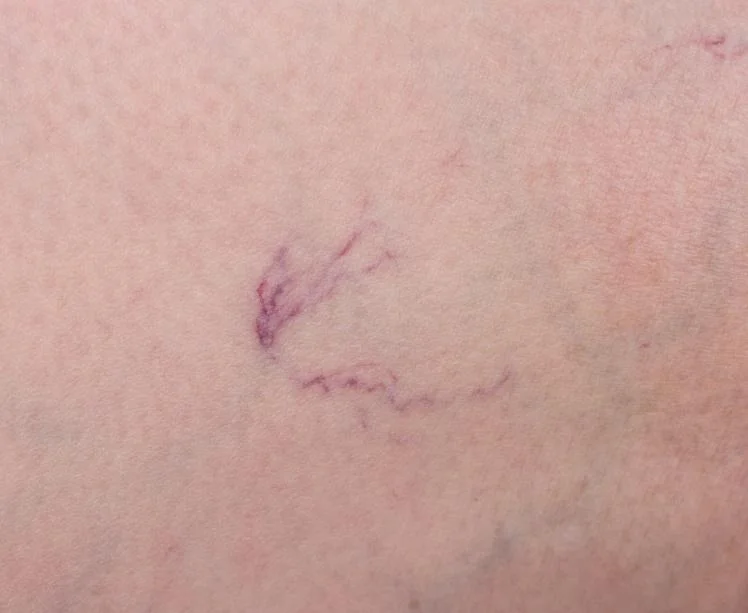
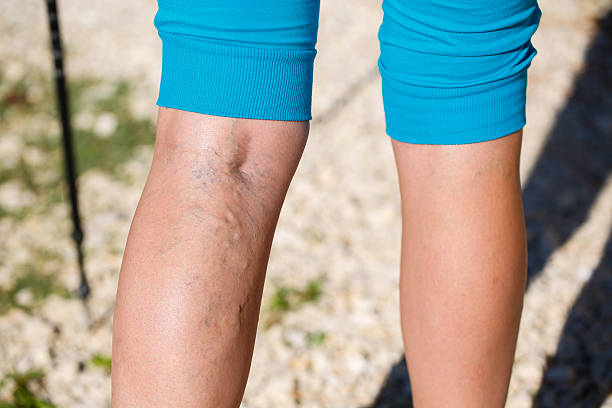
Varicose veins are enlarged, swollen, and twisted veins that often appear blue or dark purple. They occur when the valves in the veins don’t function properly, leading to blood pooling in the veins instead of flowing back to the heart. This condition is most commonly found in the legs, but it can occur in other parts of the body as well.
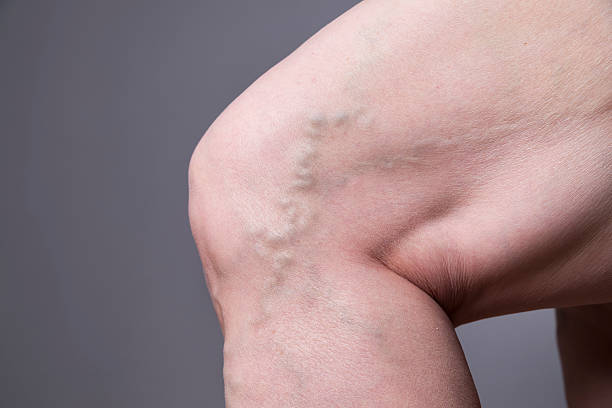
Causes of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins develop when the valves in the veins weaken or become damaged, leading to blood pooling and veins becoming enlarged and twisted. Several factors can contribute to this weakening of the vein valves, including genetics, age, prolonged standing or sitting, obesity, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause), and a history of blood clots or vein disorders. These factors can increase the pressure within the veins, causing them to stretch and bulge, ultimately resulting in the formation of varicose veins. Understanding these causes can help individuals take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment to manage varicose veins effectively.
Risk Factors
Varicose veins develop due to weakened or damaged valves in the veins. Several factors can increase the risk of developing varicose veins, including:
- Age: Aging causes wear and tear on the valves in the veins.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, pre-menstruation, or menopause.
- Family History: Genetics play a significant role; if other family members have varicose veins, the risk is higher.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Occupations that require long periods of standing or sitting can decrease blood circulation.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
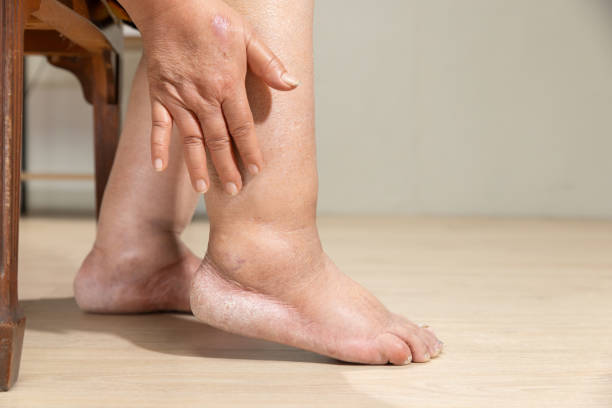
Varicose veins often manifest with various symptoms that can range from mild discomfort to more severe complications. Common symptoms include visible, twisted, and bulging veins, typically blue or purple in color, that are easily noticeable under the skin. Individuals with varicose veins may also experience sensations of heaviness, achiness, or throbbing in the affected area, especially after prolonged periods of standing or sitting. Swelling, itching, and a feeling of restlessness in the legs are also common symptoms. In some cases, varicose veins may lead to more serious complications such as skin ulcers, bleeding, or blood clots. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for early detection and appropriate management of varicose veins to prevent further complications.
Complications
Varicose veins are not just a cosmetic concern; they can cause discomfort and lead to more serious health issues. Common symptoms include:
- Swollen, twisted veins are the most visible sign of varicose veins.
- Aching pain and discomfort: often worse after standing or sitting for long periods.
- Swelling: Particularly in the lower legs.
- Skin Changes: dry, itchy, and thinner skin over the affected vein.
- Leg cramps: especially at night.
If left untreated, varicose veins can lead to complications such as:
- Ulcers: Painful ulcers can form on the skin near varicose veins, particularly near the ankles.
- Blood Clots: Superficial thrombophlebitis (a blood clot in a vein close to the surface of the skin) can cause swelling and pain.
- Bleeding: Varicose veins close to the skin may burst and cause minor bleeding.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for varicose veins range from conservative measures like lifestyle changes and compression stockings to minimally invasive procedures such as sclerotherapy and endovenous laser treatment. These procedures aim to alleviate symptoms, improve appearance, and prevent complications associated with varicose veins. In more severe cases, surgical interventions like vein stripping or ambulatory phlebectomy may be necessary. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the most suitable treatment approach based on individual needs and the severity of varicose veins.
Surgical Treatments
Various treatments are available to manage and alleviate the symptoms of varicose veins, ranging from lifestyle changes to medical procedures.
Lifestyle changes and home remedies
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve circulation and reduce pressure in the veins.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the pressure on the veins.
- Elevation: Elevating the legs can help improve blood flow.
- Compression stockings: These can help squeeze the legs, aiding blood flow and reducing swelling.
Medical Procedures
For more severe cases, several medical procedures can effectively treat varicose veins:
- Sclerotherapy: A solution is injected into the vein, causing it to scar and close.
- Laser Treatments: Laser light is used to close off smaller varicose veins and spider veins.
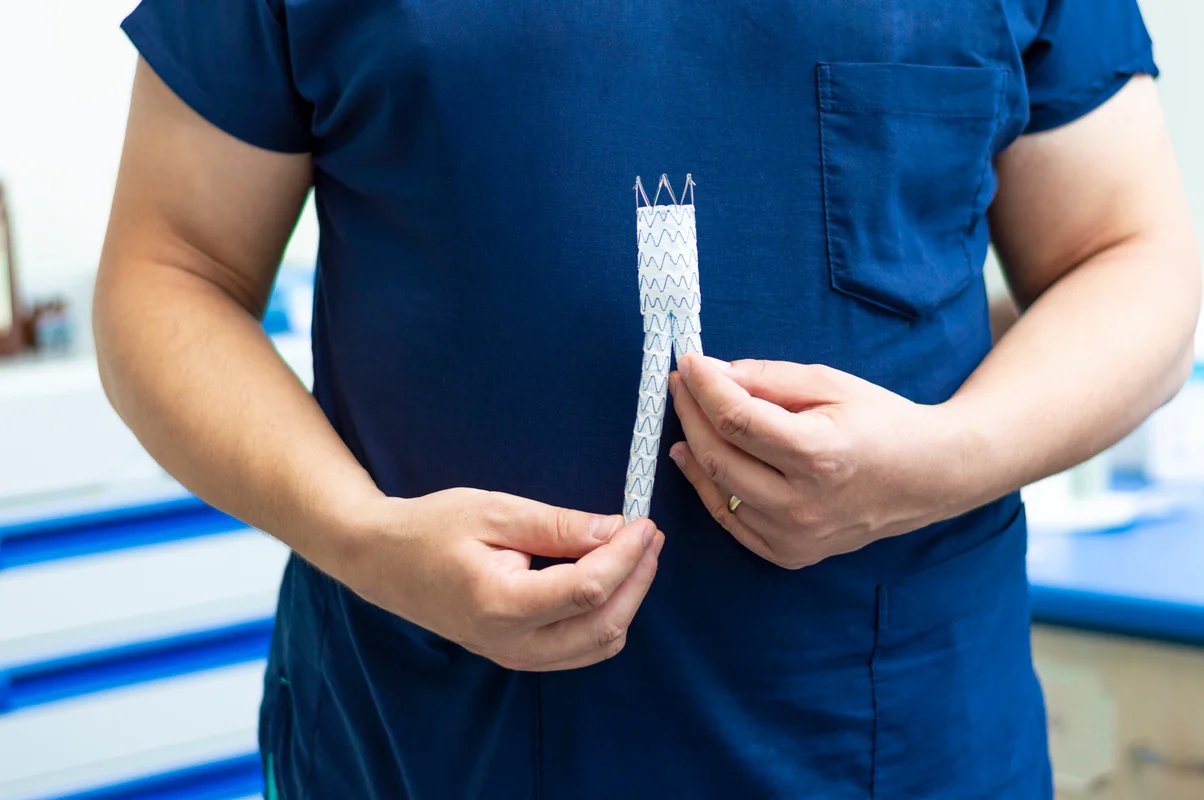
- Catheter-assisted Procedures: A catheter is inserted into the vein, and the tip is heated to close the vein.
- Vein Stripping: In severe cases, veins may be surgically removed through small incisions.
- Endovenous Ablation Therapy: Uses heat from radiofrequency or lasers to close off varicose veins.
Struggling with Varicose Veins?
Explore safe and effective treatment options with Dr. Darryl Lim.

Conclusion
Understanding varicose veins involves recognizing the causes, identifying symptoms, and exploring the wide range of treatment options available. While lifestyle changes can help manage mild cases, more advanced treatments are available for severe cases, ensuring relief from the discomfort and potential complications associated with varicose veins.