In summary:
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is reduced blood flow to the legs due to narrowing or blockage of the leg arteries. It is often caused by atherosclerosis and increases overall cardiovascular risk. Patients may experience calf cramps when walking that ease with rest (claudication), numbness, cold feet, poorly healing foot wounds, or even gangrene. Diagnosis is usually with duplex ultrasound (and sometimes CT angiography). Treatment depends on symptoms and severity, ranging from risk-factor optimisation and lifestyle changes to minimally invasive angioplasty and stenting to restore blood flow.
What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?
Peripheral Vascular Disease (also known as Peripheral Arterial Disease, PAD) is a circulation problem where blood flow to the legs becomes restricted, usually because the leg arteries have narrowed from fatty plaque build-up (atherosclerosis). Many people only discover it when walking becomes uncomfortable, or when a foot wound just won’t heal.
The good news is that early diagnosis makes a big difference. With the right treatment plan (often starting with lifestyle and medication and escalating to surgical intervention only when needed), most patients can improve symptoms and reduce the risk of serious complications.
What is Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD)?
Think of your leg arteries as “pipes” that deliver oxygen and nutrients to your muscles and skin. In peripheral vascular disease (PVD), plaque builds up along the artery walls and narrows the channel, so less blood can get through.
When physiological demand increases (for example when walking uphill, climbing stairs, or walking for longer distances) the leg muscles may not receive enough oxygenated blood. This typically shows up as cramping, tightness, heaviness, or fatigue in the calves (and sometimes the thighs or buttocks), which improves with rest.
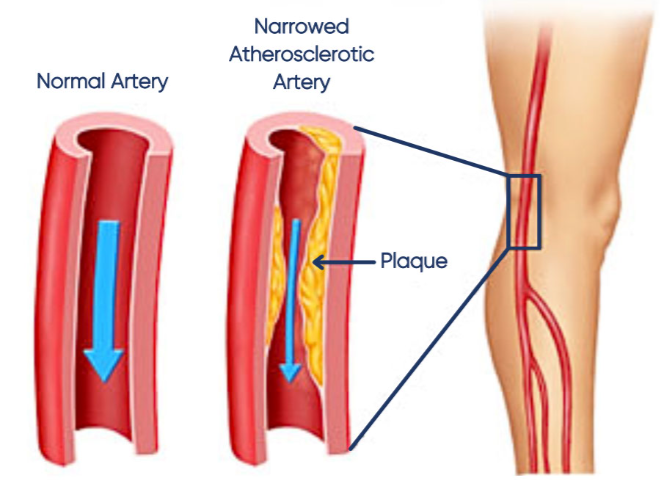
In more severe cases, reduced blood flow compromises oxygen and nutrient delivery to the skin and soft tissue in the foot. This may present as slow-healing wounds, infection, and in some cases tissue loss and gangrene can occur if not treated promptly.
Common symptoms of PVD (and what patients often describe)
Symptoms can be subtle at the start, and some people have no symptoms at all.
Typical symptoms include:
- Calf pain, tightness, or cramping when walking that is typically relieved with rest (intermittent claudication)
- Reduced walking distance (needing to stop more often)
- Cold feet, numbness, or “dead” feeling in the toes
- Weak or absent pulses in the feet
- Slower toenail growth, hair loss on the lower legs
- Foot wounds or ulcers that heal slowly (especially in diabetic patients)
More concerning symptoms (often later-stage):
Pain in the foot/toes at rest (worse at night)
Blackened toes, gangrene, or spreading infection
Non-healing ulcers despite good wound care
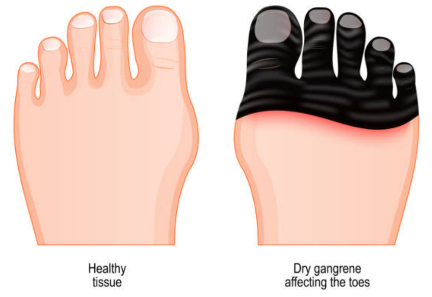
These later symptoms can indicate chronic limb-threatening ischaemia (CLTI), which needs prompt vascular assessment.
Why PVD matters (it’s not just a “leg problem”)
PVD is often a sign of more widespread atherosclerosis. In other words, the same plaque build-up affecting the leg arteries may also be present in the arteries supplying the heart and brain. So treating PVD isn’t only about walking comfort- it’s also about reducing your long-term cardiovascular risk.
What causes PVD? Who is at higher risk?
The main cause is atherosclerosis. Risk increases with:
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Kidney disease (especially patients who are already on dialysis)
- Older age
- Family history of cardiovascular disease
In Singapore, the most common “high-risk combo” we see is diabetes + smoking history + slow healing foot wounds, often with reduced sensation (neuropathy) masking how serious the circulation issue has become.
The “Triple Whammy” in Diabetes
Diabetic patients can be particularly vulnerable when a new foot wound develops, because several factors often stack up at the same time:
1) Slower healing and poorer tissue quality
Diabetes can impair immune response and microcirculation, so wounds tend to heal more slowly.
2) Reduced sensation from neuropathy
Nerve damage can cause numbness (often in a glove-and-stocking pattern), so patients may not even realise they have a blister or small cut until it becomes infected or more advanced.
3) More severe arterial disease to the foot
Diabetes accelerates atherosclerosis and can lead to heavy calcification and blockage of the arteries supplying the foot, reducing the blood flow needed for healing.
When these three factors occur together, foot wounds can worsen quickly — which is why early assessment and prompt treatment matter so much in diabetic patients.
How PVD is assessed
A good assessment is more than a quick look at the feet.
It usually includes:
- A focused history (walking distance, rest pain, wound history, diabetes/smoking)
- Pulse and circulation exam (including foot temperature and capillary refill)
- Duplex arterial ultrasound to map blood flow and identify where arteries are narrowed
- If more extensive or higher-up disease is suspected (for example, in the iliac arteries in the pelvis or the aorta), a CT peripheral angiogram may be arranged to define the anatomy and plan treatment
And importantly- if symptoms and examination don’t match (for example, pain that sounds more nerve-related or back-related), the assessment should consider alternate causes rather than forcing everything into “circulation”.
Treatment Options for PVD
Treatment for peripheral vascular disease is highly personalised, and depends on a careful assessment of symptom severity, limb threat, arterial anatomy, functional goals, and baseline cardiovascular risk. For many people, the first step is optimising risk factors and a structured walking programme to improve symptoms and support long-term cardiovascular health.
Others require revascularisation (restoring blood flow)- particularly when walking distance is severely limited, when there is rest pain, or when a foot wound is simply not healing.
1) Foundation treatment (recommended for almost everyone)
The starting point is usually to reduce the drivers of atherosclerosis and improve overall vascular health. This often includes:
- Smoking cessation (one of the most important modifiable factors)
- Optimising diabetes, blood pressure and cholesterol
- Antiplatelet therapy and statin therapy when appropriate
These measures do not “remove” existing plaque overnight, but they significantly reduce progression and lower the risk of cardiovascular events over time.
2) Structured exercise therapy (for walking pain, also called “claudication”)
For patients with intermittent claudication, a structured walking programme (sometimes supervised) is a core part of treatment. Done consistently, it can improve walking distance, reduce symptoms, and meaningfully improve quality of life.
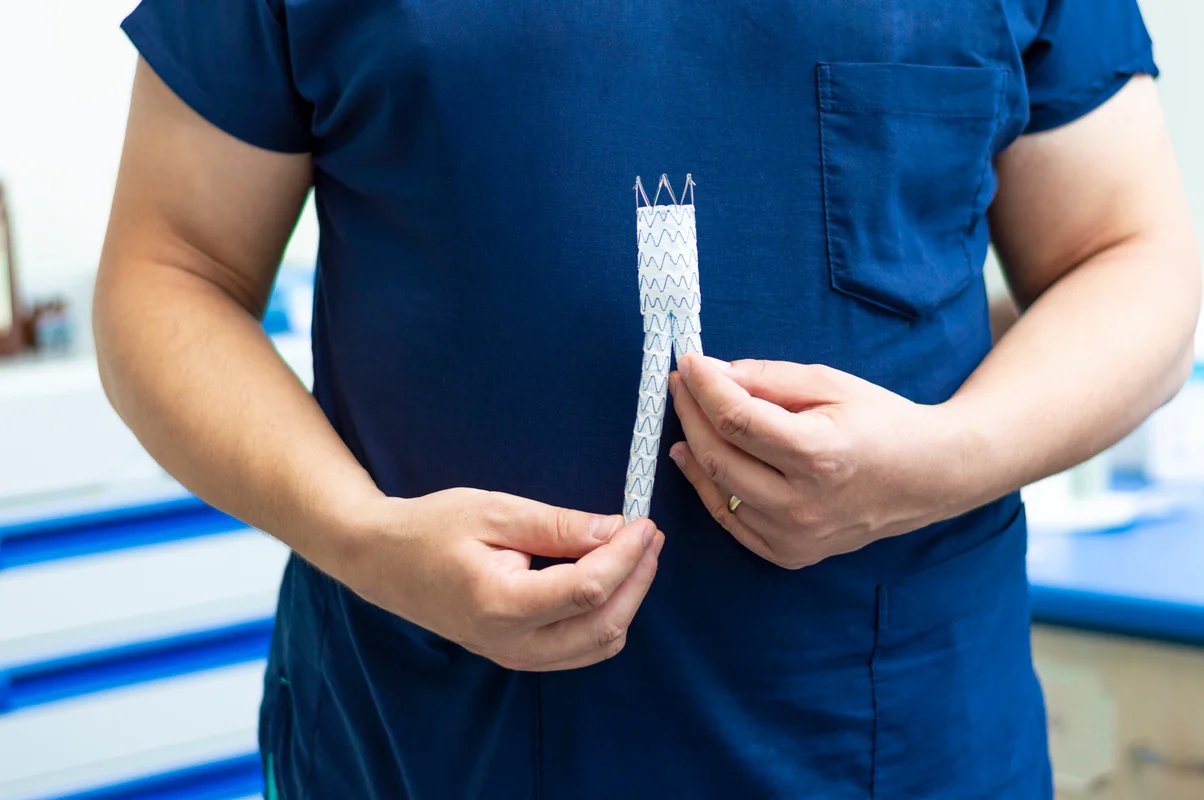
3) Minimally invasive endovascular treatment: Angioplasty and Stenting
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive way to open a narrowed artery. A small puncture (usually in the groin) allows a slender catheter to reach the blockage under X-ray guidance. A balloon is inflated to widen the artery, and a stent may be placed to help keep it open.
If a narrowed artery is causing significant pain or preventing wound healing, minimally invasive endovascular treatment is often the first-line approach. This may involve:
- Balloon angioplasty (to widen the narrowed segment)
- Stenting (when needed to support the artery and keep it open)
These procedures are typically performed through a small puncture site. Many patients can go home the same day or the next day, depending on complexity and overall health.
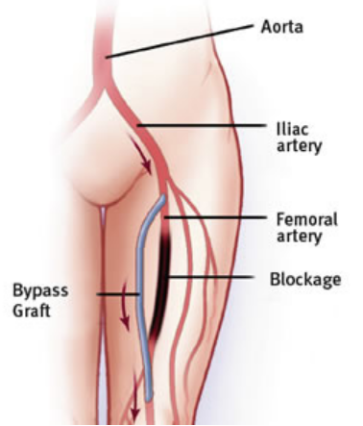
4) Surgical bypass (when anatomy or disease severity calls for it)
Bypass surgery may be considered for more extensive disease, particularly in limb-threatening situations where endovascular options are less suitable.
5) Advanced limb salvage strategies for severe disease (CLTI)
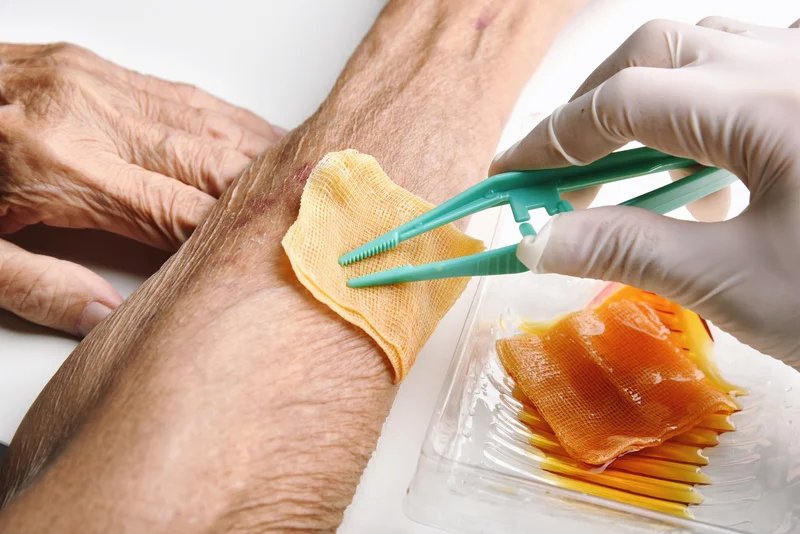
In advanced cases (especially diabetes-related foot wounds with poor blood supply), limb salvage often requires a multi-pronged approach. That may include:
- Revascularization to optimise blood flow
- Wound debridement to clean the non-viable tissue, or even to amputate gangrenous toes
- Meticulous wound care after surgery to ensure wounds heal adequately
This is the group where timing matters. Once chronic limb-threatening ischaemia (CLTI) is present, the goal is to restore enough blood flow for healing and reduce the risk of tissue loss.
If you’d like a detailed assessment and a clear plan, Dr Darryl Lim is a vascular and endovascular surgeon in Singapore with a special interest in complex endovascular interventions, including limb salvage. He has performed over 3,000 interventional procedures, and in appropriate limb-salvage cases, outcomes are consistently strong. Where appropriate, treatment can be planned around duplex and imaging findings to target the true blockage pattern and maximise wound-healing.
At Risk of Peripheral Vascular Disease?
PVD can progress silently until serious symptoms appear. Early detection and proper care can help preserve mobility and save limbs.

When to seek urgent assessment
Seek urgent medical review if you have:
- A cold, pale, blue foot/toes
- Rapidly worsening pain or numbness
- Foot wounds with spreading redness, discharge, or fever
- Blackened toes/skin changes suggestive of tissue loss
These can signal severe ischaemia or infection risk that should not wait.
When it’s worth booking a vascular consult
It’s worth getting checked if you’re noticing any of the following:
- Calf cramps or tightness when walking that eases with rest
- A reduced walking distance over weeks to months
- Cold feet, numb toes, or frequent “mysterious” foot injuries
- Any foot wound that isn’t improving steadily
When these symptoms show up, early diagnosis and clarity helps. Dr Darryl Lim can assess your symptoms and, when indicated, map the narrowed segments with duplex ultrasound, so treatment targets the true problem rather than guesswork.
FAQ about Peripheral Vascular Disease
Is PVD the same as PAD?
In day-to-day use, “PVD” often interchangeably refers to peripheral artery disease (PAD) in the legs- reduced arterial blood flow due to atherosclerosis.
What are the early signs of PVD in the legs?
Walking-related calf cramps/tightness, reduced walking distance, cold feet, numbness, and slow-healing wounds are common early signs.
Can PVD be cured?
PVD is usually not “cured” in the sense of reversing all plaque, but it can be very well managed. Symptom control and complication prevention are the goals, and many patients improve significantly with the right plan.
Does everyone with PVD need angioplasty or surgery?
No. Many patients do well with lifestyle optimisation, medication, and structured exercise. Procedures are usually reserved for significant symptoms, poor quality of life, or limb/wound-threatening disease.
Why are foot wounds such a big deal in diabetes?
Because diabetes can reduce sensation (neuropathy) and weaken healing. When that overlaps with reduced blood flow, small injuries can escalate quickly.