Vascular Specialist for Aortic Aneurysm
An aortic aneurysm is a dangerous condition where the aorta—the body’s largest blood vessel—weakens and bulges. If left untreated, it can rupture and cause life-threatening internal bleeding. The right doctor to consult for aortic aneurysm is a vascular specialist, typically a vascular surgeon, who has the expertise to diagnose and treat complex conditions of the arteries and veins.
Why See a Vascular Specialist for an Aortic Aneurysm?
Vascular surgeons are trained to manage both routine and high-risk vascular conditions, including aneurysms of the thoracic aorta (chest) and abdominal aorta (abdomen). They can:
Diagnose aneurysms with imaging tools such as CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds.
Assess the size and location of the aneurysm to determine treatment urgency.
Offer surgical and minimally invasive procedures to prevent rupture.
Provide long-term monitoring for patients with smaller aneurysms.
Treatment Options for Aortic Aneurysms
The best treatment depends on the aneurysm’s location, size, and the patient’s overall health. Options include:
Open surgical repair—The weakened section of the aorta is replaced with a synthetic graft through a major incision. This is a durable, long-term solution.
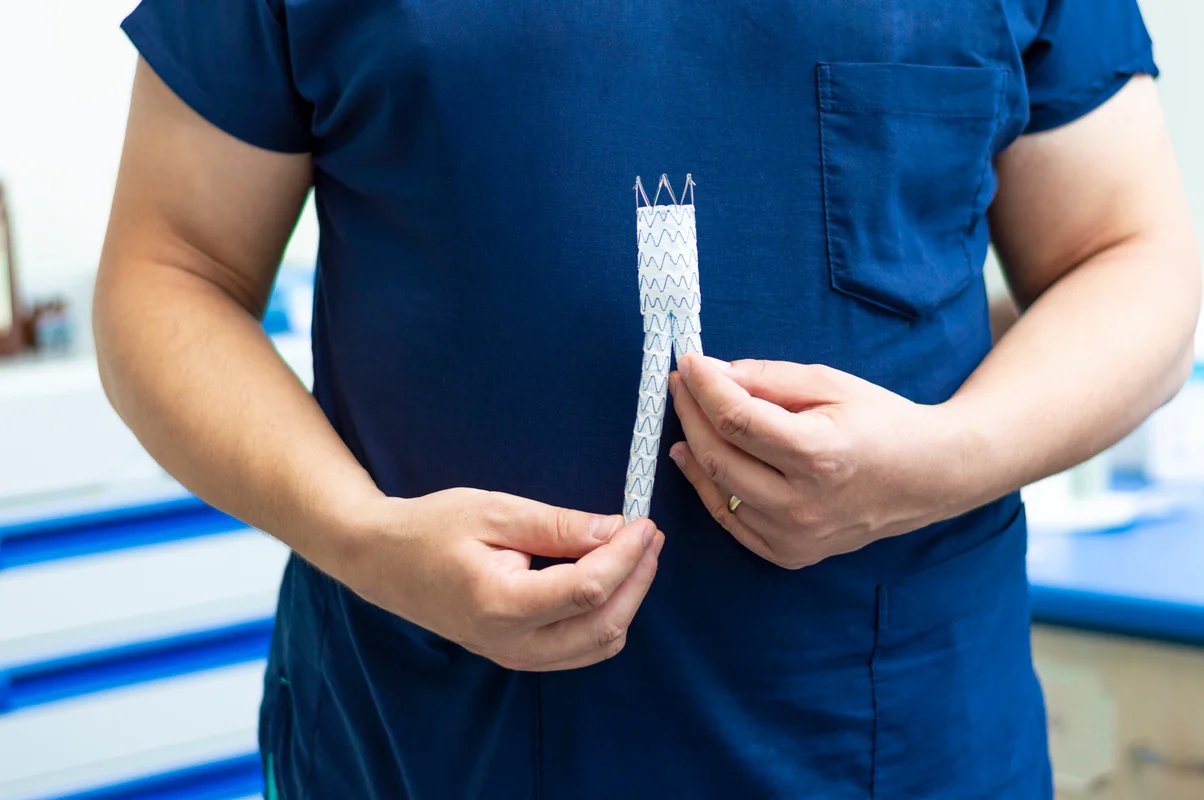
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR/TEVAR)—A minimally invasive procedure where a stent graft is inserted through small incisions in the groin and guided into the aorta. Recovery is quicker, making it suitable for higher-risk patients.
Both approaches reinforce the aorta, reducing the risk of rupture.
Diagnosing and Monitoring Aortic Aneurysms
A vascular specialist will use advanced imaging to confirm and monitor aneurysms:
Ultrasound—often the first test used for screening abdominal aneurysms.
CT angiography—provides detailed images of the aorta.
MRI – occasionally used for complex or follow-up evaluations.
Small aneurysms may only require regular imaging and lifestyle management, while larger ones often need immediate treatment.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
An aortic aneurysm may not cause symptoms until it becomes large or ruptures. Seek emergency help if you experience:
Sudden, severe chest, back, or abdominal pain.
Rapid pulse, dizziness, or fainting.
Signs of internal bleeding.
Early screening is especially important for men over 65 with a history of smoking or patients with a family history of aneurysms.
Final Thoughts
A vascular specialist for aortic aneurysm, usually a vascular surgeon, provides life-saving expertise through open surgical repair or minimally invasive endovascular techniques. By diagnosing, monitoring, and treating aneurysms before they rupture, vascular specialists protect patients from severe complications and improve long-term health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What type of doctor treats an aortic aneurysm?
An aortic aneurysm should be evaluated and treated by a vascular surgeon. They specialize in the diagnosis and management of blood vessel diseases, including complex arterial conditions like aneurysms.
2. What causes an aortic aneurysm to develop?
Aneurysms often result from atherosclerosis (plaque buildup), high blood pressure, smoking, genetic disorders, or age-related vessel weakening. Regular screening is crucial for those at risk.
3. How serious is an aortic aneurysm?
It can be life-threatening if it ruptures, causing severe internal bleeding. Early detection through imaging and proper management by a vascular specialist can prevent rupture and save lives.
4. How do doctors decide between open surgery and EVAR/TEVAR?
The choice depends on the aneurysm’s size, location, and your overall health. Minimally invasive options like EVAR or TEVAR are ideal for certain patients, while others may benefit from open repair for longer-term durability.
5. Can an aortic aneurysm be cured without surgery?
Small aneurysms that aren’t growing quickly can often be managed with regular monitoring, blood pressure control, smoking cessation, and lifestyle changes. However, surgery or endovascular repair is the only way to definitively fix a large or expanding aneurysm.
6. Is recovery faster after endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR)?
Yes. Most patients recover within 1–2 weeks after EVAR or TEVAR, compared to 4–8 weeks for open repair. Your vascular surgeon will guide post-procedure care and follow-up imaging.

Take the First Step Towards Vascular Health Today!
Are you ready to transform your vascular health with expert care and cutting-edge treatments?
Dr. Darryl Lim and his dedicated team are committed to providing personalized, compassionate care. Whether you’re dealing with varicose veins, peripheral artery disease, or other vascular conditions, Dr. Lim’s expertise and innovative approach ensure you receive the best possible outcomes.

Dr. Darryl Lim is a Senior Consultant Vascular and Endovascular Surgeon at the Novena Vascular and Varicose Vein Centre in Singapore. Before this role, he served as the Director of the Vascular Unit at Changi General Hospital and as a Service Chief at the Singhealth-Duke NUS Vascular Centre. Under his tenure, Changi General Hospital’s Vascular Unit was recognized as a regional centre of excellence.
Dr. Lim has a strong commitment to training emerging interventionalists and enhancing the capabilities of vascular units in Southeast Asia. He is regularly invited to travel to regional units to conduct live case workshops and to speak at international conferences.