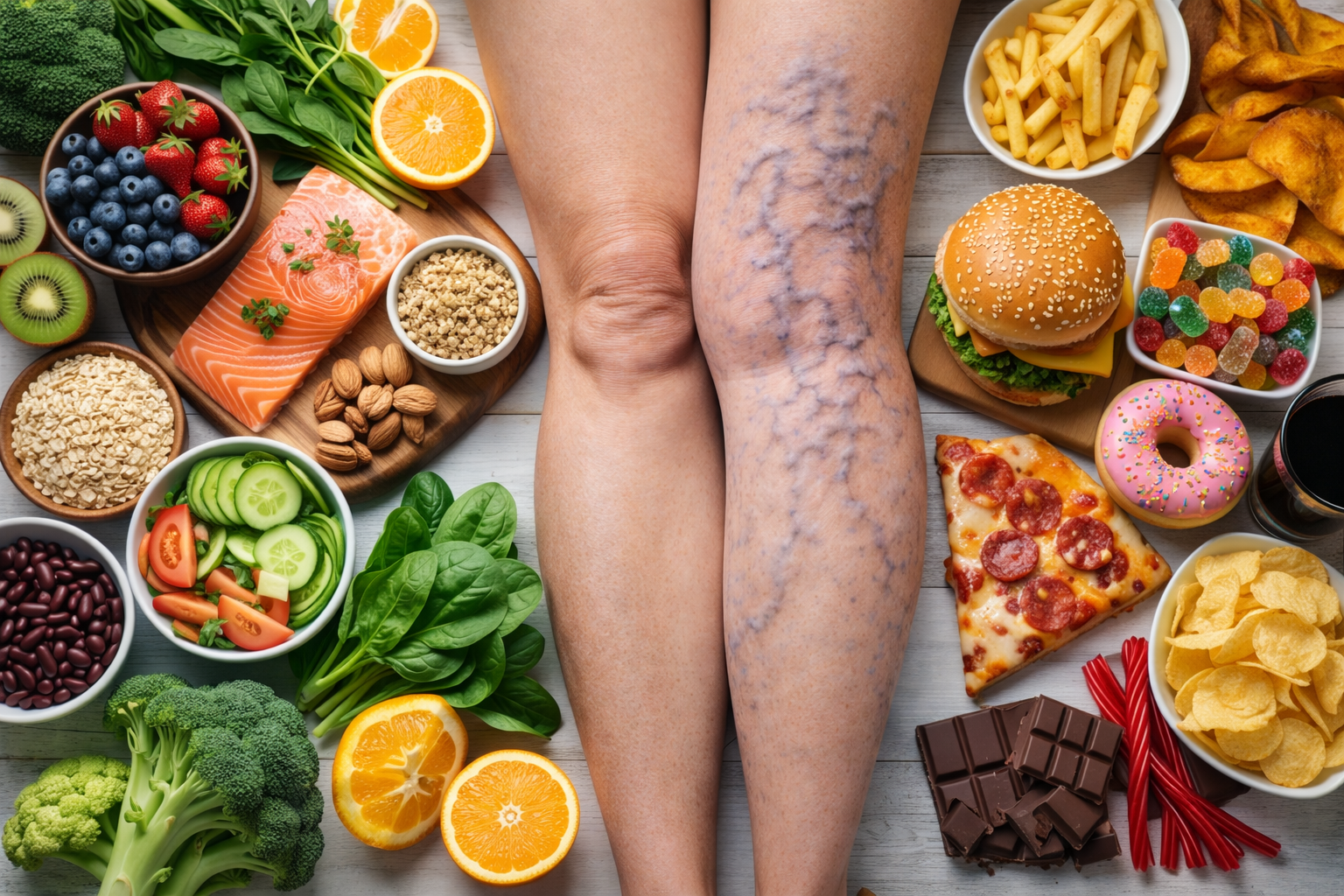
Early detection of peripheral artery disease (PAD) is crucial to preventing serious health complications and improving patient outcomes. PAD, a condition where arteries in the legs become narrowed or blocked, can lead to pain, mobility issues, and even limb loss if left untreated. Early diagnosis allows for timely interventions such as lifestyle changes, medications, and minimally invasive procedures like angioplasty and stenting to restore proper blood flow. Detecting PAD early also helps manage the associated risks of heart attack and stroke, as PAD is often linked to atherosclerosis in other parts of the body. Regular screenings and awareness of symptoms are key to catching PAD in its initial stages, ensuring better overall vascular health and quality of life.

What is peripheral artery disease?
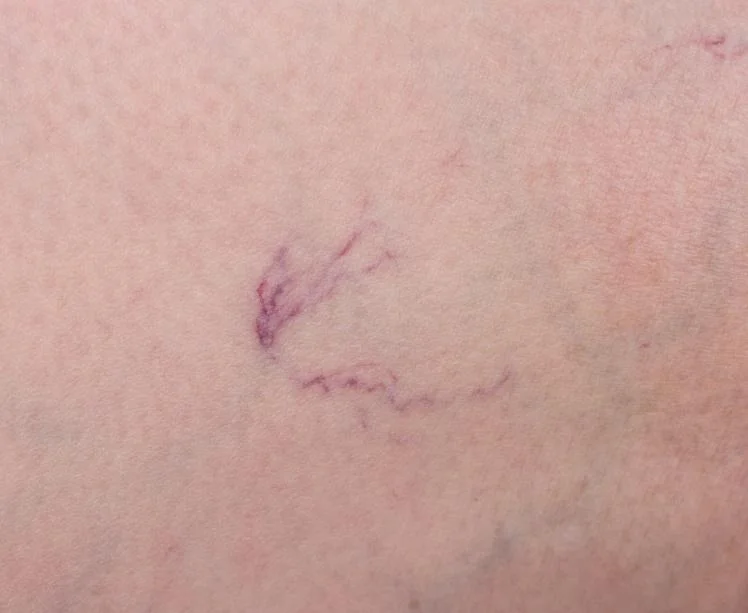
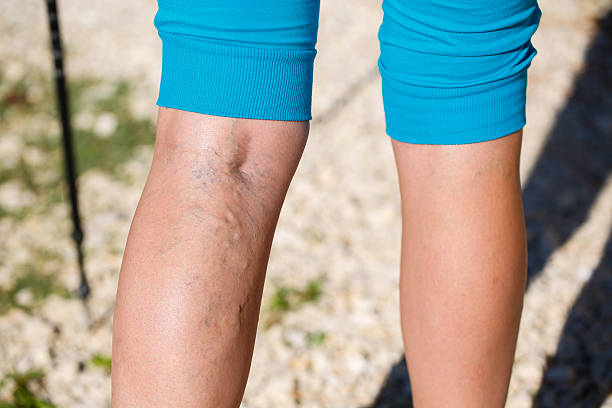
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to your limbs. When you develop PAD, your extremities, usually your legs, don’t receive enough blood flow to keep up with demand. This can cause symptoms such as leg pain when walking (claudication). PAD is also likely to be a sign of a more widespread accumulation of fatty deposits in your arteries (atherosclerosis). This condition may be reducing blood flow to your heart and brain, as well as your legs.
Symptoms of PAD
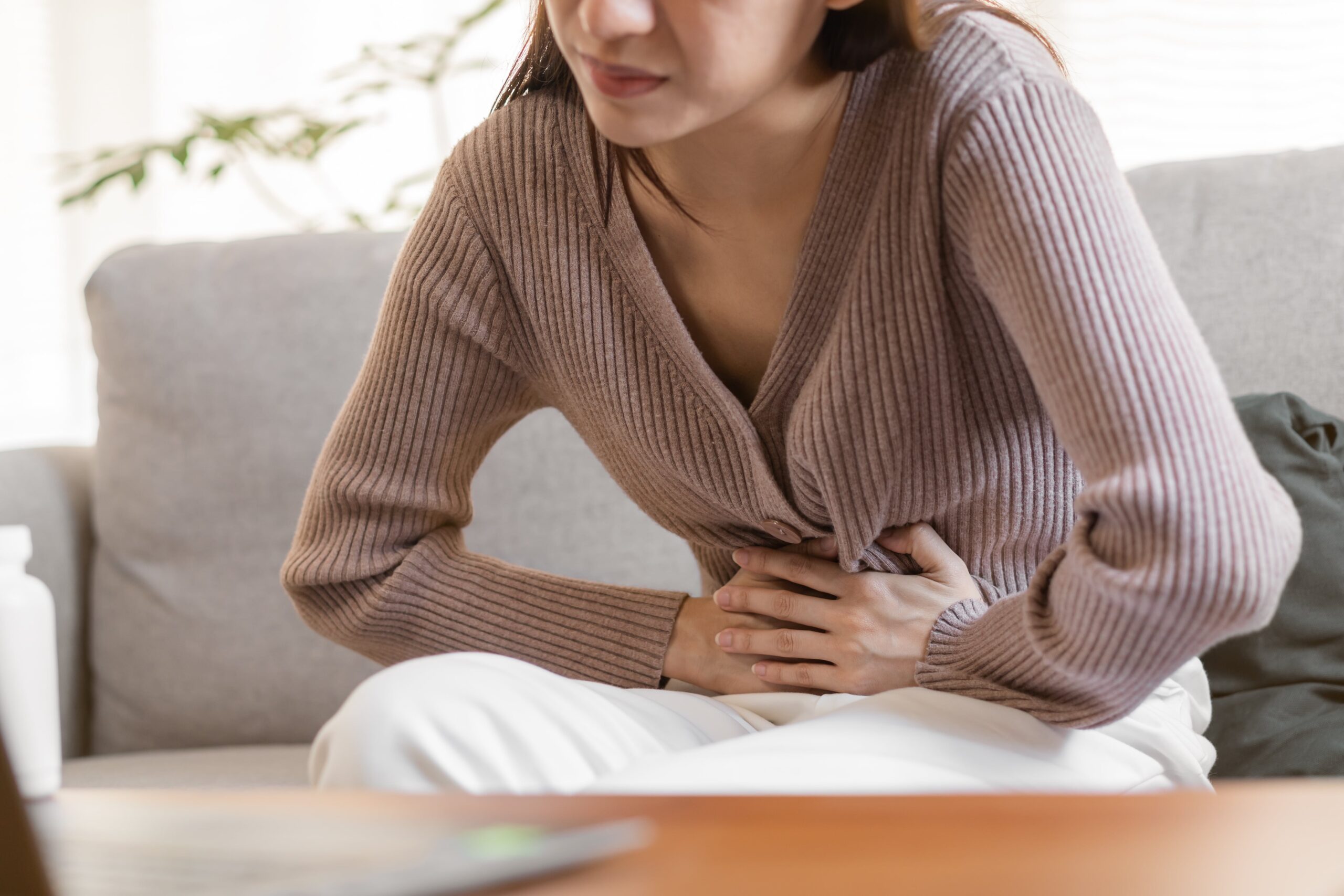
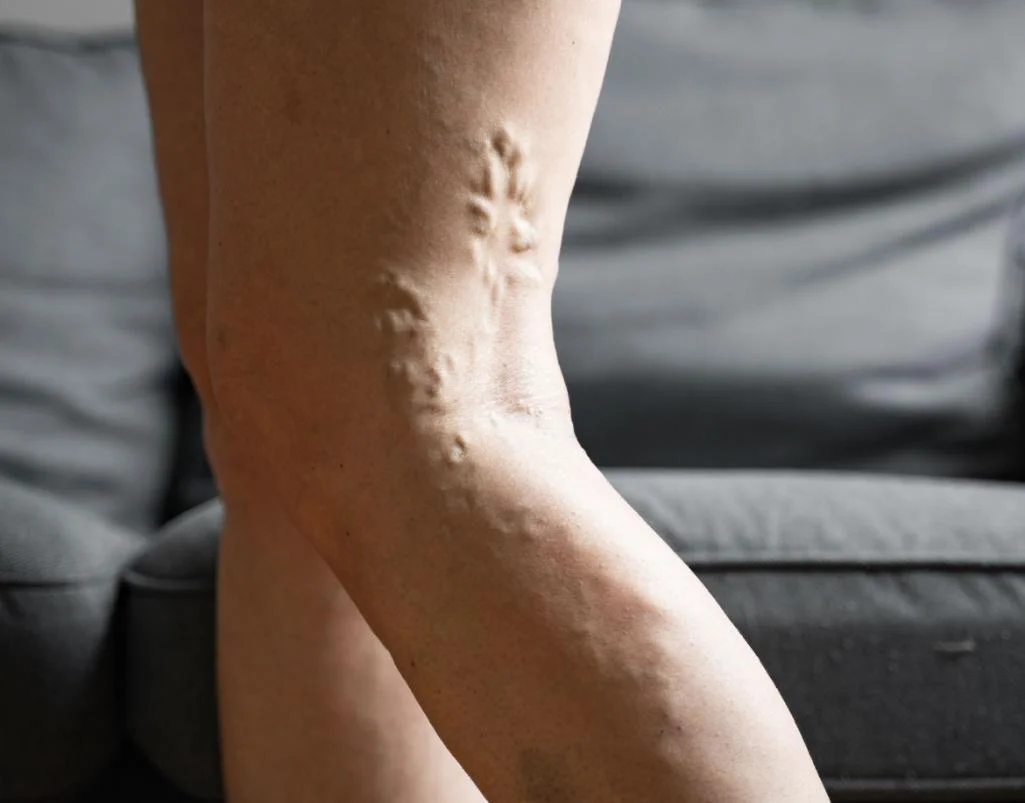
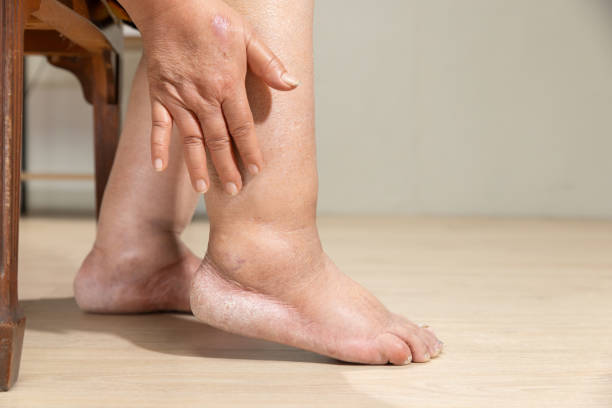
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) often presents with a range of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Common signs include leg pain or cramping during physical activities like walking or climbing stairs, known as claudication, which typically subsides with rest. Other symptoms may include numbness, weakness, or a feeling of heaviness in the legs, coldness in the lower leg or foot, and sores or wounds on the toes, feet, or legs that heal slowly or not at all. In advanced cases, PAD can lead to changes in skin color and the loss of hair on the legs. Recognizing these symptoms early is essential for seeking timely medical evaluation and treatment to prevent complications.
Early warning signs
PAD often goes undiagnosed because its symptoms can be mild or mistaken for other conditions. Recognizing the early signs is crucial for timely treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Leg Pain When Walking: Known as claudication, this pain typically occurs in the calf and is relieved by rest.
- Leg Numbness or Weakness: Reduced blood flow can lead to sensations of numbness or weakness in the legs.
- Coldness in Your Lower Leg or Foot: Especially when compared with the other leg.
- Sores on Toes, Feet, or Legs: Wounds that heal slowly or not at all.
- A Change in the Color of Your Legs: Pale or bluish skin.
- Hair loss or slower hair growth: on your feet and legs.
Why Early Detection is Crucial
Early detection of peripheral artery disease (PAD) is vital for preventing severe health complications and enhancing treatment outcomes. Identifying PAD in its initial stages allows for prompt intervention, which can halt the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and limb amputation. Early detection enables the implementation of lifestyle changes, medication management, and minimally invasive procedures to improve blood flow and overall vascular health. Additionally, diagnosing PAD early can help uncover other underlying cardiovascular conditions, facilitating comprehensive care. By catching PAD early, patients have a better chance of maintaining their mobility, quality of life, and long-term health.
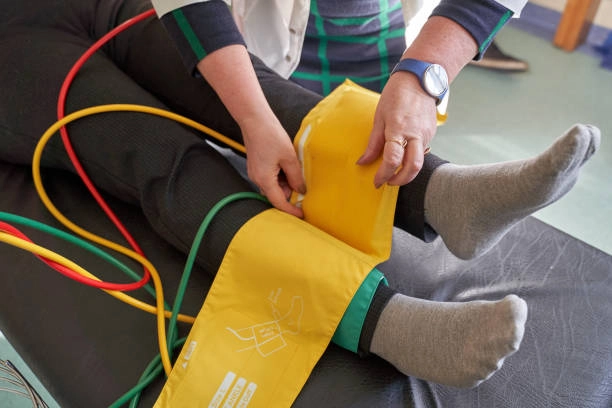

Health Risks
Early detection of PAD is vital to prevent complications such as:
- Heart Attack and Stroke: PAD is a marker for systemic atherosclerosis, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
- Critical Limb Ischemia: severe blockage in the arteries of the lower extremities, which can lead to pain, ulcers, and limb loss.
- Reduced Mobility: Claudication can limit your physical activities, impacting your quality of life.
Methods for Early Detection
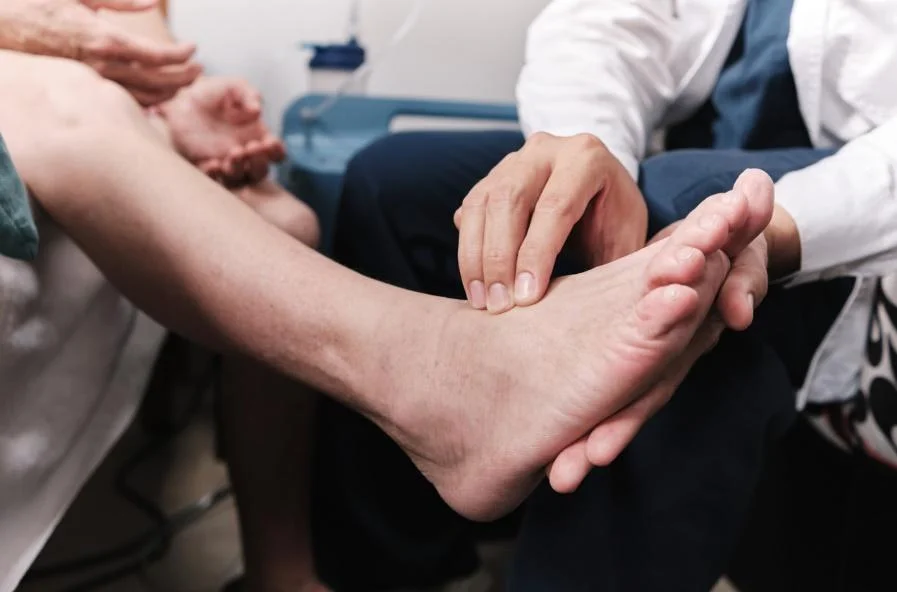
Several methods can aid in the early detection of peripheral artery disease (PAD). Ankle-brachial index (ABI) testing is a commonly used diagnostic tool that compares blood pressure measurements in the ankle and arm to assess peripheral circulation. Doppler ultrasound imaging can visualize the blood flow in the arteries and identify areas of blockage or narrowing. Additionally, physicians may conduct physical examinations to assess symptoms such as leg pain, skin changes, or diminished pulses. Patient history, including risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, and hypertension, also plays a crucial role in identifying individuals at higher risk for PAD. Regular screenings, especially for individuals over 50 or with risk factors, are essential for early detection and timely intervention to prevent complications.
Screening Techniques
Early detection methods for PAD involve both non-invasive and minimally invasive techniques, including:
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): This simple test compares the blood pressure in your ankle with the blood pressure in your arm. A low ABI can indicate reduced blood flow and PAD.
- Doppler Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to measure the blood flow in your arteries.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) provides detailed images of blood vessels.
- Computed Tomographic Angiography (CTA) uses X-rays to create detailed images of your arteries.
- Blood tests: to check for conditions related to PAD, such as high cholesterol and diabetes.
Diagnostic Tests
In addition to screening techniques, diagnostic tests can provide a more detailed assessment:
- The treadmill exercise test measures the severity of symptoms and the effect on blood pressure during exercise.
- Angiography involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels and taking X-rays to show the flow of blood through the arteries.
At Risk of Peripheral Vascular Disease?
PVD can progress silently until serious symptoms appear. Early detection and proper care can help preserve mobility and save limbs.

Conclusion
Early detection of peripheral artery disease (PAD) is paramount for effective management and prevention of severe complications associated with this condition. Regular screenings, particularly for individuals deemed at high risk due to factors such as age, smoking, diabetes, and hypertension, play a pivotal role in identifying PAD in its early stages. Timely interventions, guided by early detection, can significantly enhance the quality of life for patients by alleviating symptoms, preserving mobility, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke. Consulting with your healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most appropriate screening and diagnostic options tailored to your individual risk factors and health status. By proactively addressing PAD through early detection and intervention, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining their vascular health and overall well-being.