Discoloration of the toes, particularly when they appear black or darkened, can be alarming. For individuals with diabetes, changes in toe color may indicate a serious underlying issue, such as poor blood circulation or tissue damage, which can lead to complications like gangrene. Understanding the potential causes and seeking timely medical attention are essential for effective treatment and prevention. In Singapore, Dr. Darryl Lim specializes in diagnosing and managing foot-related complications in diabetic patients, helping them maintain foot health and prevent serious issues.
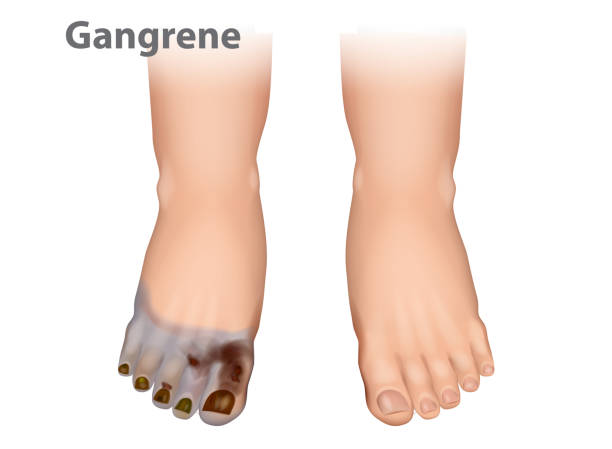
Common Causes of Black or Darkened Toes
Several factors may cause the toes to turn black or darken. Some of these are benign, but others require immediate medical attention, especially in diabetic individuals who are more susceptible to foot complications. Here are some of the most common causes:
- Poor Blood Circulation (Peripheral Vascular Disease): Diabetic patients are at increased risk of peripheral vascular disease (PVD), a condition where blood vessels narrow, restricting blood flow to the extremities. Insufficient blood flow deprives the tissues of oxygen, leading to a dark or blackened appearance in severe cases.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: Nerve damage in the feet can reduce sensation, making it difficult for patients to feel injuries or pressure points. This lack of awareness often leads to unnoticed wounds that can worsen over time, causing discoloration and other complications like infection. Unfortunately, the condition is sometimes quite advanced by the time it is detected.
- Trauma or Injury: Trauma to the toe, such as stubbing or dropping something on it, can lead to bruising and darkened skin. While minor injuries may heal on their own, diabetics should monitor them closely as poor circulation can impair healing.
- Gangrene: A lack of blood supply to the tissue can lead to gangrene, causing the skin to turn black as tissue dies. Gangrene is a severe condition requiring immediate treatment to prevent the spread of infection and further complications.
- Fungal Infections: Black toenails may result from fungal infections that spread and cause the nail to darken. Fungal infections are more common in people with diabetes due to the warm, moist environment inside shoes and compromised immune response.
Each of these causes requires a tailored approach to treatment, making it essential for patients to consult a medical professional if they notice any unusual discoloration in their toes.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Black or Darkened Toes
Not every case of darkened toes is cause for alarm, but diabetic individuals should be particularly cautious. Seek medical attention if you notice:
- Persistent black, blue, or darkened discoloration that doesn’t improve over time.
- Additional symptoms such as swelling, pain, or foul odor.
- Numbness or tingling in the affected toes, which may indicate nerve damage.
- Blisters, open sores, or wounds that are slow to heal.
Dr. Lim provides specialized care for diabetic foot health, offering prompt evaluation and treatment to address issues before they worsen.
Diagnostic Process for Blackened Toes
A thorough evaluation is conducted to determine the cause of toe discoloration and guide appropriate treatment. The diagnostic process may include:
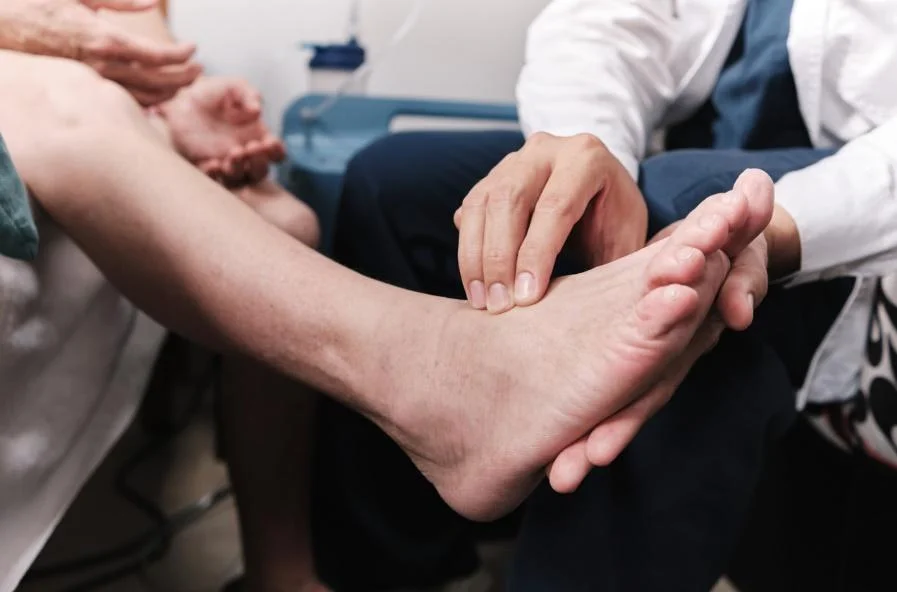
- Physical Examination: Dr. Lim will examine the affected area for signs of infection, injury, or other visible abnormalities.
- Blood Flow Assessment: Poor circulation is a common cause of toe discoloration in diabetic patients. If deemed necessary, blood flow may be assessed using a duplex ultrasound or other diagnostic tools to identify the presence and location of any blockages.
- Nerve Testing: Diabetic neuropathy can reduce sensation in the feet. Testing nerve function helps determine if nerve damage is contributing to the issue.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check blood glucose levels and assess overall health, as high blood sugar can contribute to poor circulation and slow healing.
Treatment Options for Blackened Toes
The appropriate treatment for blackened toes depends on the underlying cause. Common treatment options include:
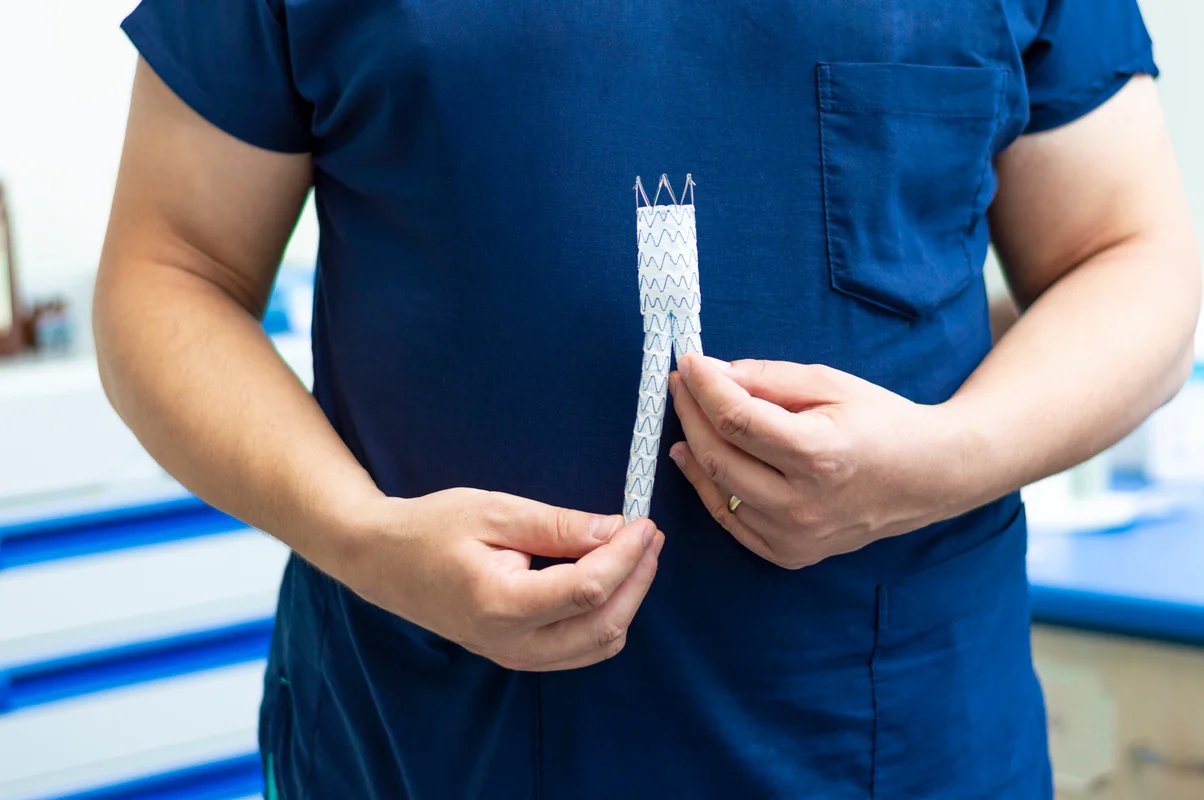
- Optimizing Blood Circulation: If poor circulation contributes to non-healing wounds, treatments such as angioplasty and stenting can be employed to unblock narrowed or clogged vessels. Restoring proper blood flow enhances oxygen and nutrient delivery to the affected area, promoting faster and more effective healing.
- Infection Control: Fungal or bacterial infections require specific treatments. Antifungal medication or antibiotics may be prescribed, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
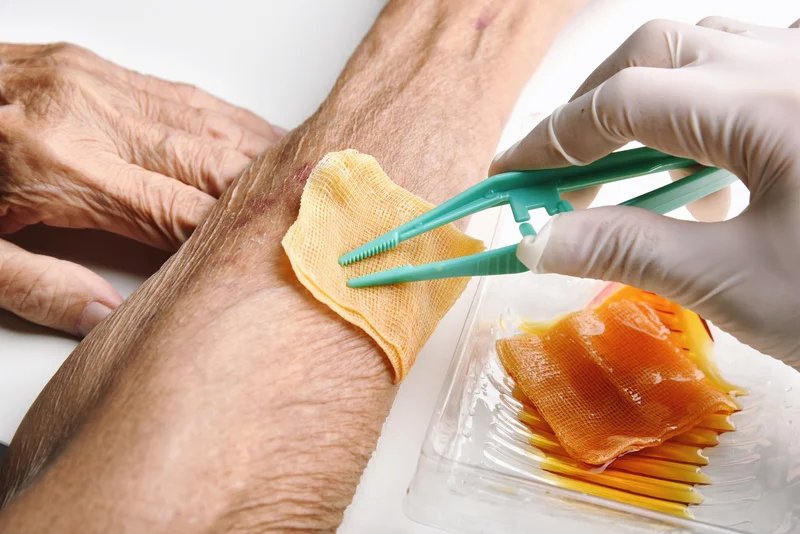
- Wound Care: For patients with open sores or blisters, proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. Dr. Lim’s clinic provides specialized wound care to manage diabetic foot wounds.
- Debridement: In cases where gangrene or dead tissue is present, debridement (removal of dead tissue) may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection and encourage healing.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): HBOT can help increase oxygen levels in the blood, promoting tissue healing and combating infection. It is often used in more severe cases where blood flow is compromised.
Each treatment plan is customized to address the specific needs and health condition of the patient, ensuring a targeted approach for effective recovery.
Preventing Toe Discoloration in Diabetic Patients
Although not all cases of blackened toes can be prevented, diabetic patients can take proactive steps to protect their foot health and minimise the risk of complications:
- Inspect Feet Daily: Perform regular self-checks to spot any changes in colour, cuts, blisters, or swelling early. Prompt attention to minor issues can prevent them from escalating into serious problems.
- Manage blood sugar levels: Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is vital for reducing the risk of neuropathy and improving circulation—both critical for protecting foot health.
- Wear proper footwear: Choose shoes that fit well, provide adequate support, and minimise pressure points to prevent injuries, bruising, or sores.
- Trim nails properly: Always trim nails straight across to avoid ingrown nails, which can lead to infections and discolouration if untreated.
- Keep Feet Clean and Dry: Daily washing and thorough drying of your feet help maintain hygiene and prevent fungal infections.
- Promote Circulation: Engage in regular exercise, avoid smoking, and consider elevating your feet when resting to improve blood flow.
Patient education and personalised care plans are essential for helping diabetic individuals adopt these preventive measures. By incorporating them into their daily routines, patients can achieve better foot health and significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Dealing with Diabetic Foot Problems?
Diabetes can lead to serious foot complications if not addressed early. Get expert care to protect your feet and prevent further issues.

Conclusion
If you notice your toes turning black or darkened, seeking medical attention is essential, especially for individuals with diabetes. Discoloration may indicate serious issues such as poor circulation, infection, or even gangrene. Dr. Darryl Lim provides expert care to diagnose and treat diabetic foot complications, helping patients preserve foot health and prevent severe outcomes.